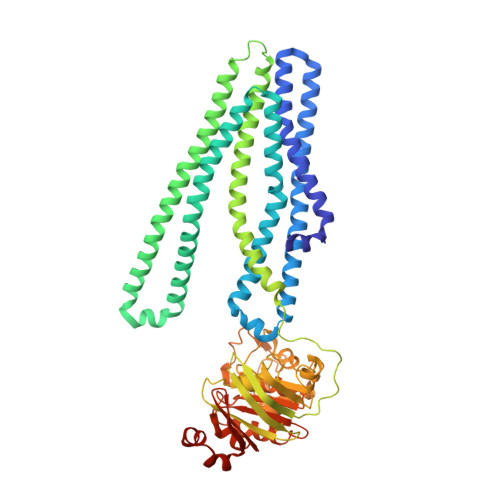
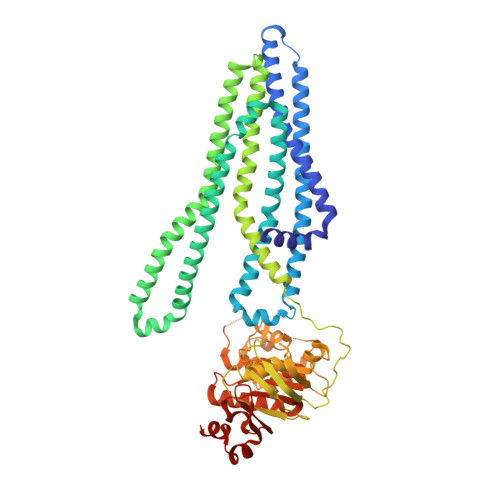
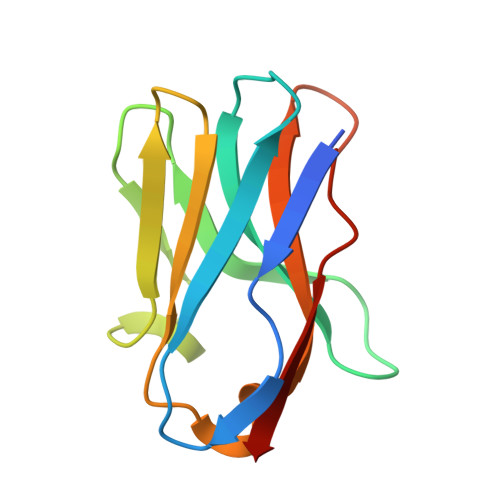
Deep mutational scan of a drug efflux pump reveals its structure-function landscape.
Meier, G., Thavarasah, S., Ehrenbolger, K., Hutter, C.A.J., Hurlimann, L.M., Barandun, J., Seeger, M.A.(2023) Nat Chem Biol 19: 440-450
- PubMed: 36443574
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-022-01205-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7OCY - PubMed Abstract:
Drug efflux is a common resistance mechanism found in bacteria and cancer cells, but studies providing comprehensive functional insights are scarce. In this study, we performed deep mutational scanning (DMS) on the bacterial ABC transporter EfrCD to determine the drug efflux activity profile of more than 1,430 single variants. These systematic measurements revealed that the introduction of negative charges at different locations within the large substrate binding pocket results in strongly increased efflux activity toward positively charged ethidium, whereas additional aromatic residues did not display the same effect. Data analysis in the context of an inward-facing cryogenic electron microscopy structure of EfrCD uncovered a high-affinity binding site, which releases bound drugs through a peristaltic transport mechanism as the transporter transits to its outward-facing conformation. Finally, we identified substitutions resulting in rapid Hoechst influx without affecting the efflux activity for ethidium and daunorubicin. Hence, single mutations can convert EfrCD into a drug-specific ABC importer.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Medical Microbiology, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland.