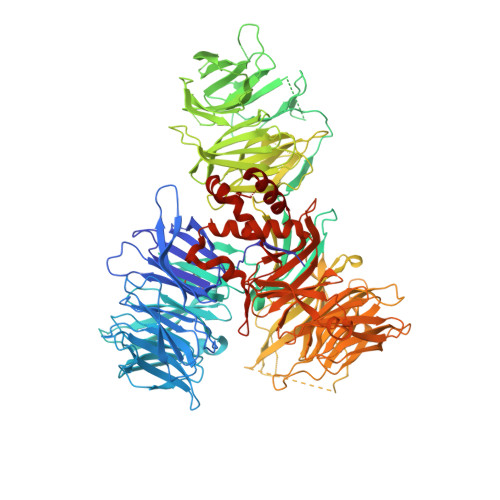
Insight into Viral Hijacking of CRL4 Ubiquitin Ligase through Structural Analysis of the pUL145-DDB1 Complex.
Wick, E.T., Treadway, C.J., Li, Z., Nicely, N.I., Ren, Z., Baldwin, A.S., Xiong, Y., Harrison, J.S., Brown, N.G.(2022) J Virol 96: e0082622-e0082622
- PubMed: 35938868
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.00826-22
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7UKN - PubMed Abstract:
Viruses evolve mechanisms to exploit cellular pathways that increase viral fitness, e.g., enhance viral replication or evade the host cell immune response. The ubiquitin-proteosome system, a fundamental pathway-regulating protein fate in eukaryotes, is hijacked by all seven classes of viruses. Members of the Cullin-RING family of ubiquitin (Ub) ligases are frequently co-opted by divergent viruses because they can target a broad array of substrates by forming multisubunit assemblies comprised of a variety of adapters and substrate receptors. For example, the linker subunit DDB1 in the cullin 4-RING (CRL4)-DDB1 Ub ligase (CRL4 DDB1 ) interacts with an H-box motif found in several unrelated viral proteins, including the V protein of simian virus 5 (SV5-V), the HBx protein of hepatitis B virus (HBV), and the recently identified pUL145 protein of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV). In HCMV-infected cells, pUL145 repurposes CRL4 DDB1 to target STAT2, a protein vital to the antiviral immune response. However, the details of how these divergent viral sequences hijack DDB1 is not well understood. Here, we use a combination of binding assays, X-ray crystallography, alanine scanning, cell-based assays, and computational analysis to reveal that viral H-box motifs appear to bind to DDB1 with a higher affinity than the H-box motifs from host proteins DCAF1 and DDB2. This analysis reveals that viruses maintain native hot-spot residues in the H-box motif of host DCAFs and also acquire favorable interactions at neighboring residues within the H-box. Overall, these studies reveal how viruses evolve strategies to produce high-affinity binding and quality interactions with DDB1 to repurpose its Ub ligase machinery. IMPORTANCE Many different viruses modulate the protein machinery required for ubiquitination to enhance viral fitness. Specifically, several viruses hijack the cullin-RING ligase CRL4 DDB1 to degrade host resistance factors. Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) encodes pUL145 that redirects CRL4 DDB1 to evade the immune system through the targeted degradation of the antiviral immune response protein STAT2. However, it is unclear why several viruses bind specific surfaces on ubiquitin ligases to repurpose their activity. We demonstrate that viruses have optimized H-box motifs that bind DDB1 with higher affinity than the H-box of native binders. For viral H-boxes, native interactions are maintained, but additional interactions that are absent in host cell H-boxes are formed, indicating that rewiring CRL4 DDB1 creates a selective advantage for the virus. The DDB1-pUL145 peptide structure reveals that water-mediated interactions are critical to the higher affinity. Together, our data present an interesting example of how viral evolution can exploit a weakness in the ubiquitination machinery.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Pharmacology, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina, USA.