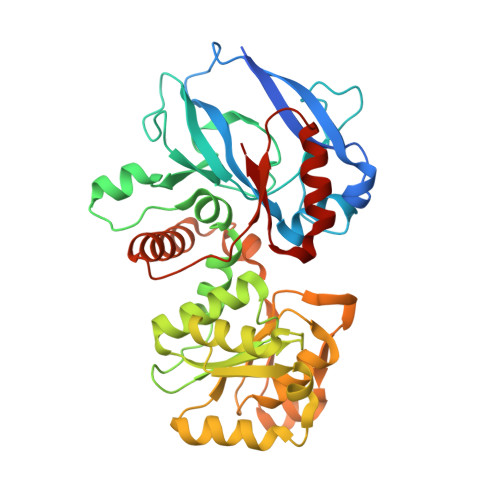
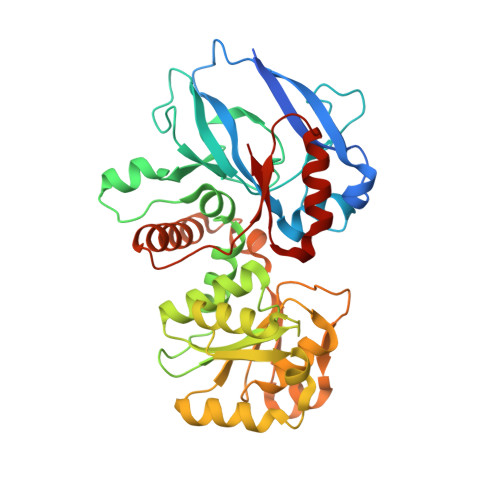
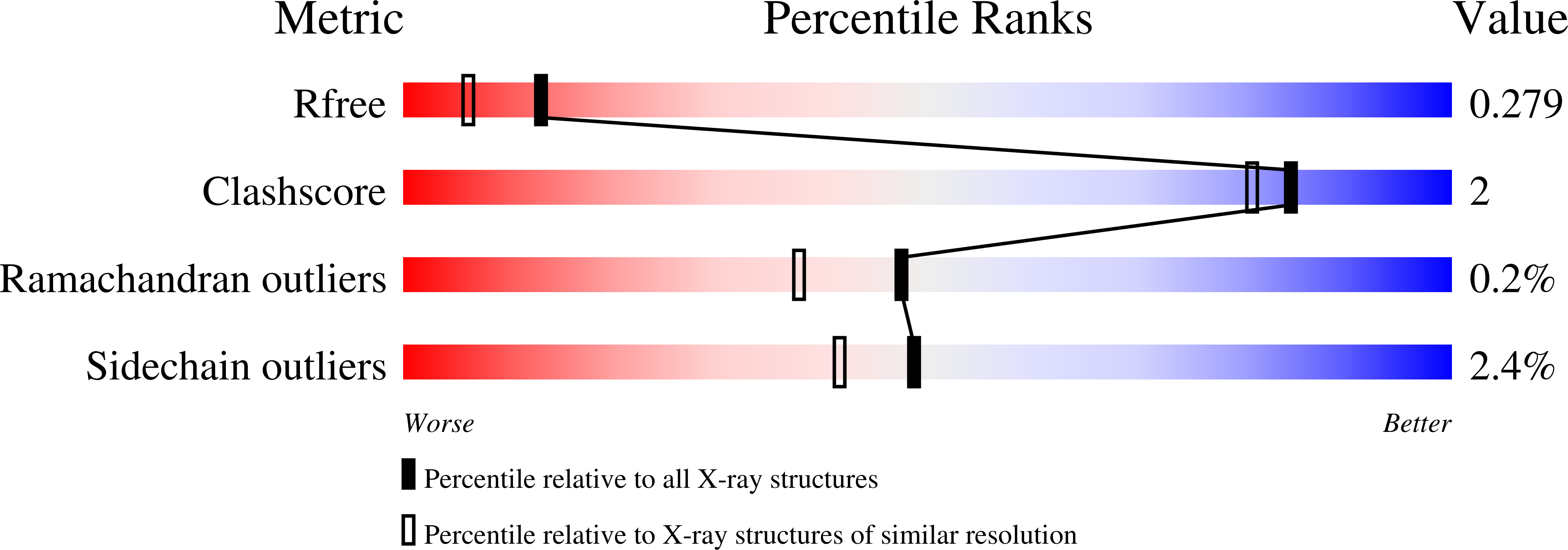Candida tropicalis expresses two mitochondrial 2-enoyl thioester reductases that are able to form both homodimers and heterodimers.
Torkko, J.M., Koivuranta, K.T., Kastaniotis, A.J., Airenne, T.T., Glumoff, T., Ilves, M., Hartig, A., Gurvitz, A., Hiltunen, J.K.(2003) J Biol Chem 278: 41213-41220
- PubMed: 12890667
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M307664200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1N9G - PubMed Abstract:
Here we report on the cloning of a Candida tropicalis gene, ETR2, that is closely related to ETR1. Both genes encode enzymatically active 2-enoyl thioester reductases involved in mitochondrial synthesis of fatty acids (fatty acid synthesis type II) and respiratory competence. The 5'- and 3'-flanking (coding) regions of ETR2 and ETR1 are about 90% (97%) identical, indicating that the genes have evolved via gene duplication. The gene products differ in three amino acid residues: Ile67 (Val), Ala92 (Thr), and Lys251 (Arg) in Etr2p (Etr1p). Quantitative PCR analysis and reverse transcriptase-PCR indicated that both genes were expressed about equally in fermenting and ETR1 predominantly respiring yeast cells. Like the situation with ETR1, expression of ETR2 in respiration-deficient Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutant cells devoid of Ybr026p/Etr1p was able to restore growth on glycerol. Triclosan that is used as an antibacterial agent against fatty acid synthesis type II 2-enoyl thioester reductases inhibited growth of FabI overexpressing mutant yeast cells but was not able to inhibit respiratory growth of the ETR2- or ETR1-complemented mutant yeast cells. Resolving of crystal structures obtained via Etr2p and Etr1p co-crystallization indicated that all possible dimer variants occur in the same asymmetric unit, suggesting that similar dimer formation also takes place in vivo.
Organizational Affiliation:
Biocenter Oulu, Department of Biochemistry, University of Oulu, Finland.