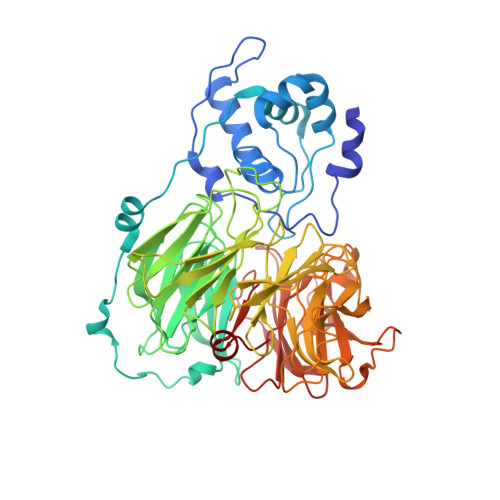
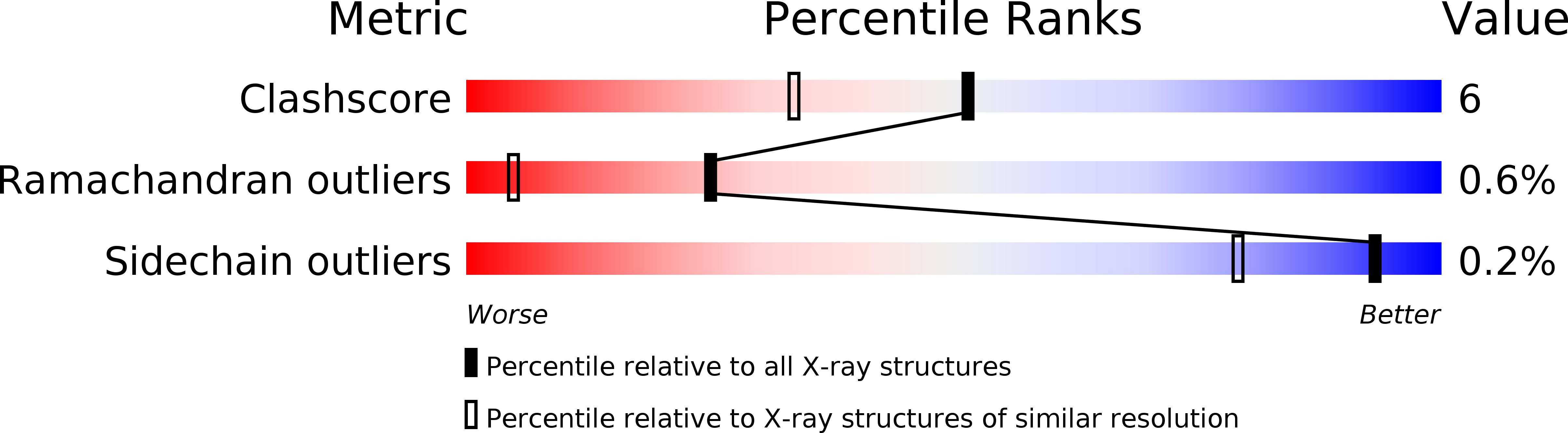The anatomy of a bifunctional enzyme: structural basis for reduction of oxygen to water and synthesis of nitric oxide by cytochrome cd1.
Fulop, V., Moir, J.W., Ferguson, S.J., Hajdu, J.(1995) Cell 81: 369-377
- PubMed: 7736589
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(95)90390-9
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1QKS - PubMed Abstract:
Cytochrome cd1-nitrite reductase is a bifunctional enzyme that catalyzes the one-electron reduction of nitrite to nitric oxide and the four-electron reduction of oxygen to water. The 1.55 A crystal structure of the dimeric enzyme from Thiosphaera pantotropha is reported here. The protein was sequenced from the X-ray structure. Each subunit contains a covalent c heme with two axial His ligands (His-17, His-69) and a unique noncovalent d1 heme ligated by Tyr-25 and His-200. The d1 heme is the mononuclear iron center where both oxygen and nitrite reduction take place. The two types of heme are located in separate domains whose arrangement suggests a mechanism requiring domain movement during catalysis.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Molecular Biophysics, University of Oxford, England.