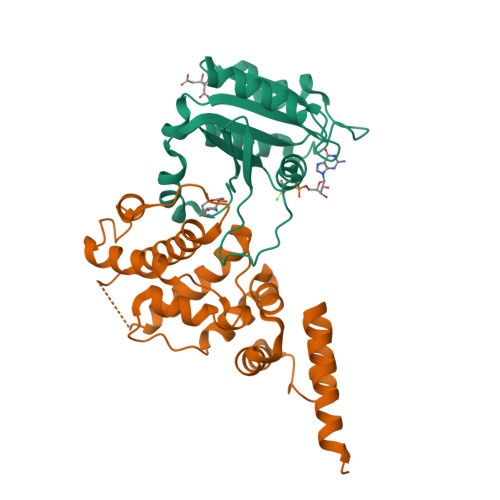
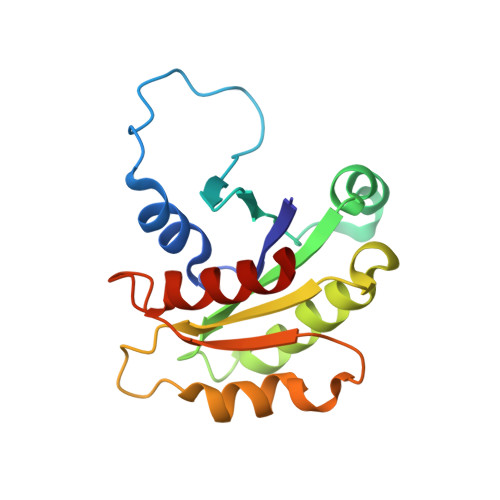
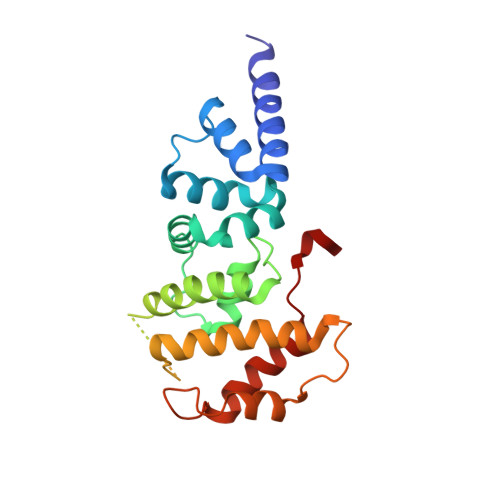
Crystal structure of ARF1*Sec7 complexed with Brefeldin A and its implications for the guanine nucleotide exchange mechanism.
Mossessova, E., Corpina, R.A., Goldberg, J.(2003) Mol Cell 12: 1403-1411
- PubMed: 14690595
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00475-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1RE0 - PubMed Abstract:
ARF GTPases are activated by guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) of the Sec7 family that promote the exchange of GDP for GTP. Brefeldin A (BFA) is a fungal metabolite that binds to the ARF1*GDP*Sec7 complex and blocks GEF activity at an early stage of the reaction, prior to guanine nucleotide release. The crystal structure of the ARF1*GDP*Sec7*BFA complex shows that BFA binds at the protein-protein interface to inhibit conformational changes in ARF1 required for Sec7 to dislodge the GDP molecule. Based on a comparative analysis of the inhibited complex, nucleotide-free ARF1*Sec7 and ARF1*GDP, we suggest that, in addition to forcing nucleotide release, the ARF1-Sec7 binding energy is used to open a cavity on ARF1 to facilitate the rearrangement of hydrophobic core residues between the GDP and GTP conformations. Thus, the Sec7 domain may act as a dual catalyst, facilitating both nucleotide release and conformational switching on ARF proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Structural Biology Program, Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, 1275 York Avenue, New York, NY 10021, USA.