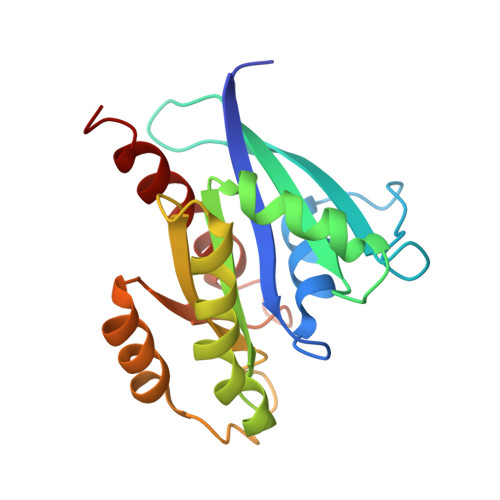
Crystal structure of the Sec4p{middle dot}Sec2p complex in the nucleotide exchanging intermediate state
Sato, Y., Fukai, S., Ishitani, R., Nureki, O.(2007) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104: 8305-8310
- PubMed: 17488829
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0701550104
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2EQB - PubMed Abstract:
Vesicular transport during exocytosis is regulated by Rab GTPase (Sec4p in yeast), which is activated by a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) called Sec2p. Here, we report the crystal structure of the Sec2p GEF domain in a complex with the nucleotide-free Sec4p at 2.7 A resolution. Upon complex formation, the Sec2p helices approach each other, flipping the side chain of Phe-109 toward Leu-104 and Leu-108 of Sec2p. These three residues provide a hydrophobic platform to attract the side chains of Phe-49, Ile-53, and Ile-55 in the switch I region as well as Phe-57 and Trp-74 in the interswitch region of Sec4p. Consequently, the switch I and II regions are largely deformed, to create a flat hydrophobic interface that snugly fits the surface of the Sec2p coiled coil. These drastic conformational changes disrupt the interactions between switch I and the bound guanine nucleotide, which facilitates the GDP release. Unlike the recently reported 3.3 A structure of the Sec4p.Sec2p complex, our structure contains a phosphate ion bound to the P-loop, which may represent an intermediate state of the nucleotide exchange reaction.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biological Information, Graduate School of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Tokyo Institute of Technology, 4259 Nagatsuta-cho, Midori-ku, Yokohama-shi, Kanagawa 226-8501, Japan.