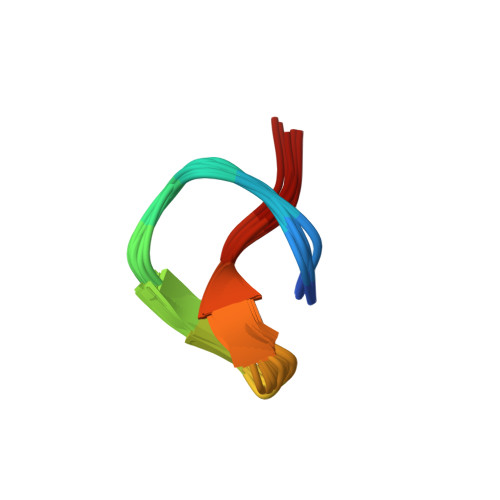
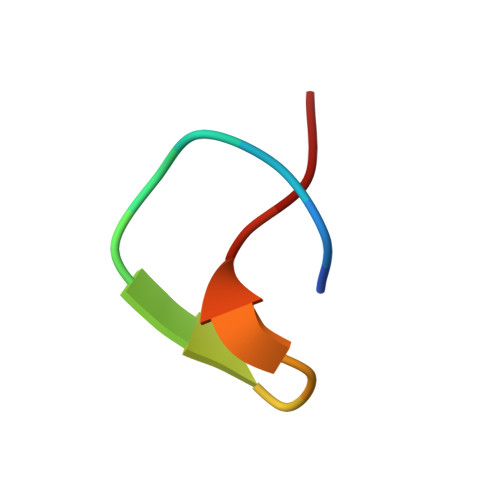
Chaxapeptin, a Lasso Peptide from Extremotolerant Streptomyces leeuwenhoekii Strain C58 from the Hyperarid Atacama Desert.
Elsayed, S.S., Trusch, F., Deng, H., Raab, A., Prokes, I., Busarakam, K., Asenjo, J.A., Andrews, B.A., van West, P., Bull, A.T., Goodfellow, M., Yi, Y., Ebel, R., Jaspars, M., Rateb, M.E.(2015) J Org Chem 80: 10252-10260
- PubMed: 26402731
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.5b01878
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2N5C - PubMed Abstract:
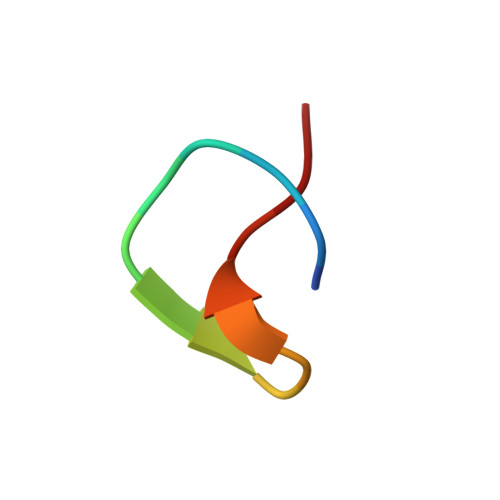
Lasso peptides are ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides (RiPPs) that possess a unique "lariat knot" structural motif. Genome mining-targeted discovery of new natural products from microbes obtained from extreme environments has led to the identification of a gene cluster directing the biosynthesis of a new lasso peptide, designated as chaxapeptin 1, in the genome of Streptomyces leeuwenhoekii strain C58 isolated from the Atacama Desert. Subsequently, 1 was isolated and characterized using high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance methods. The lasso nature of 1 was confirmed by calculating its nuclear Overhauser effect restraint-based solution structure. Chaxapeptin 1 displayed a significant inhibitory activity in a cell invasion assay with human lung cancer cell line A549.
Organizational Affiliation:
Marine Biodiscovery Centre, University of Aberdeen , Meston Walk, Aberdeen AB24 3UE, Scotland, U.K.