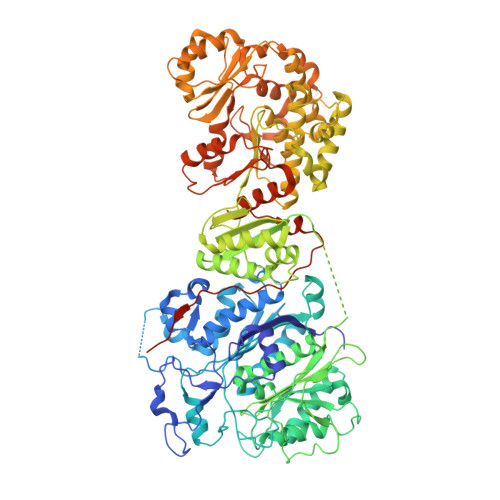
Structural and mechanistic analysis of protein interactions in module 3 of the 6-deoxyerythronolide B synthase
Tang, Y., Chen, Y.A., Kim, C.Y., Cane, E.D., Khosla, C.(2007) Chem Biol 14: 931-943
- PubMed: 17719492
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2007.07.012
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2QO3 - PubMed Abstract:
We report the 2.6 A X-ray crystal structure of a 190 kDa homodimeric fragment from module 3 of the 6-deoxyerthronolide B synthase covalently bound to the inhibitor cerulenin. The structure shows two well-organized interdomain linker regions in addition to the full-length ketosynthase (KS) and acyltransferase (AT) domains. Analysis of the substrate-binding site of the KS domain suggests that a loop region at the homodimer interface influences KS substrate specificity. We also describe a model for the interaction of the catalytic domains with the acyl carrier protein (ACP) domain. The ACP is proposed to dock within a deep cleft between the KS and AT domains, with interactions that span both the KS homodimer and AT domain. In conjunction with other recent data, our results provide atomic resolution pictures of several catalytically relevant protein interactions in this remarkable family of modular megasynthases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Keck Building, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305, USA.