Mechanism for the Hydrolysis of a Sulfur-Sulfur Bond Based on the Crystal Structure of the Thiosulfohydrolase Soxb.
Sauve, V., Roversi, P., Leath, K.J., Garman, E.F., Antrobus, R., Lea, S.M., Berks, B.C.(2009) J Biol Chem 284: 21707
- PubMed: 19535341
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.002709
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2WDC, 2WDD, 2WDE, 2WDF - PubMed Abstract:
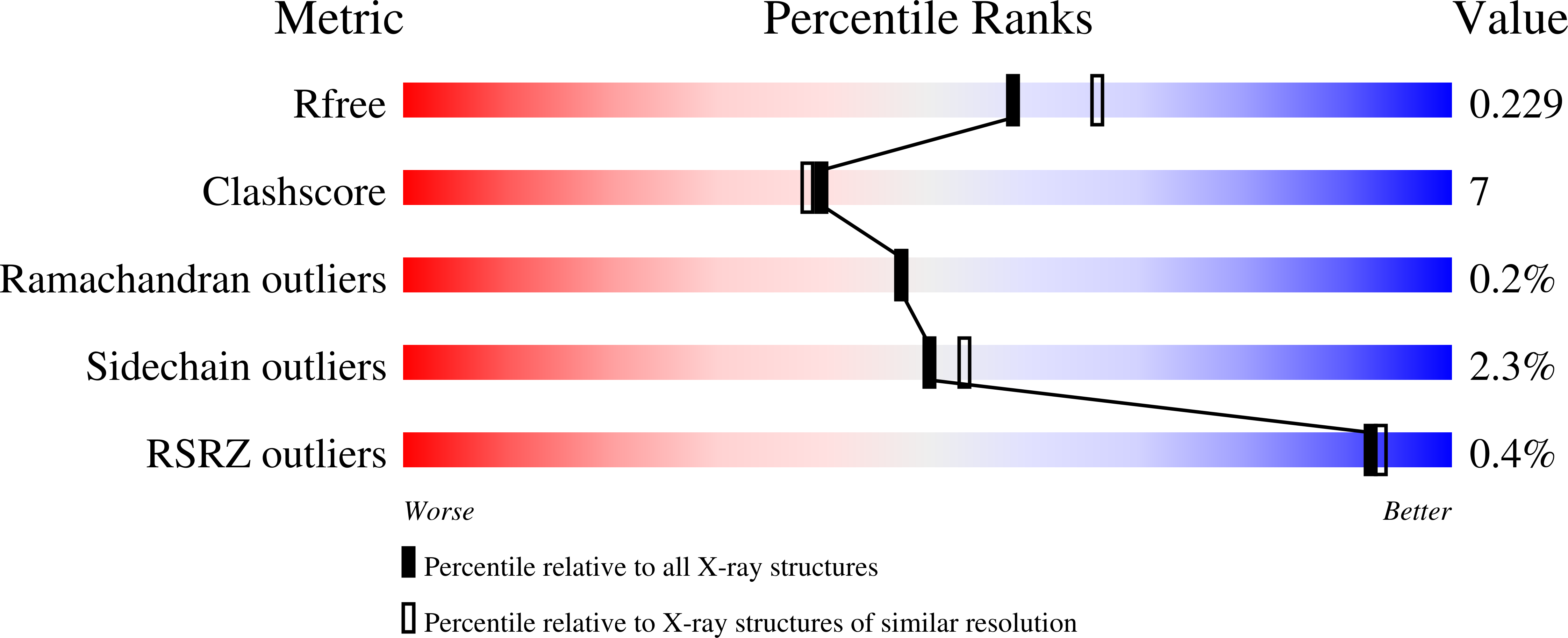
SoxB is an essential component of the bacterial Sox sulfur oxidation pathway. SoxB contains a di-manganese(II) site and is proposed to catalyze the release of sulfate from a protein-bound cysteine S-thiosulfonate. A direct assay for SoxB activity is described. The structure of recombinant Thermus thermophilus SoxB was determined by x-ray crystallography to a resolution of 1.5 A. Structures were also determined for SoxB in complex with the substrate analogue thiosulfate and in complex with the product sulfate. A mechanistic model for SoxB is proposed based on these structures.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Oxford, Oxford OX1 3QU, United Kingdom.