Insight Into the Induction Mechanism of the Gntr/Hutc Bacterial Transcription Regulator Yvoa
Resch, M., Schiltz, E., Titgemeyer, F., Muller, Y.A.(2010) Nucleic Acids Res 38: 2485
- PubMed: 20047956
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp1191
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2WV0 - PubMed Abstract:
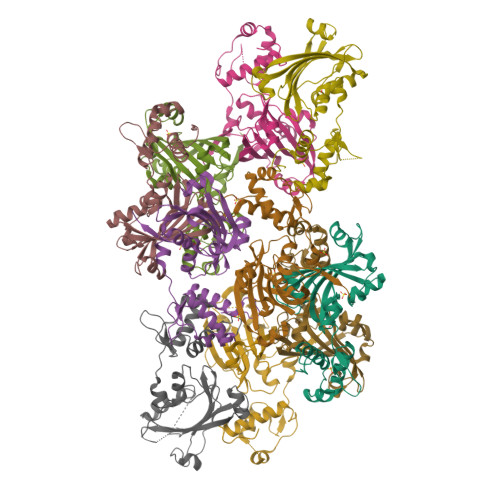
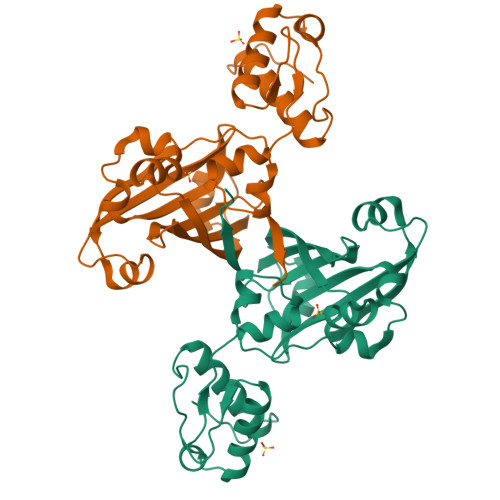
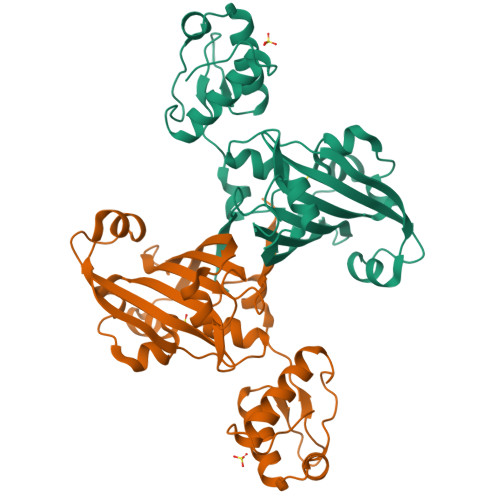
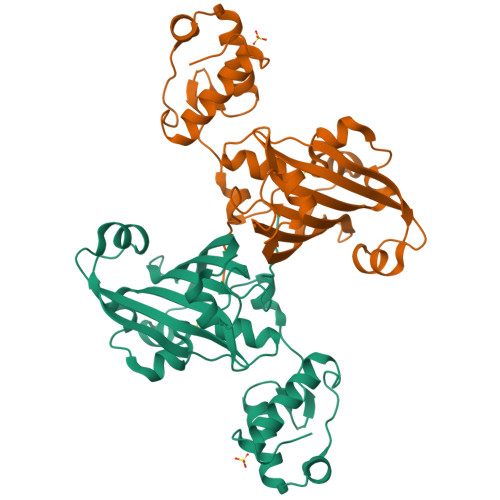
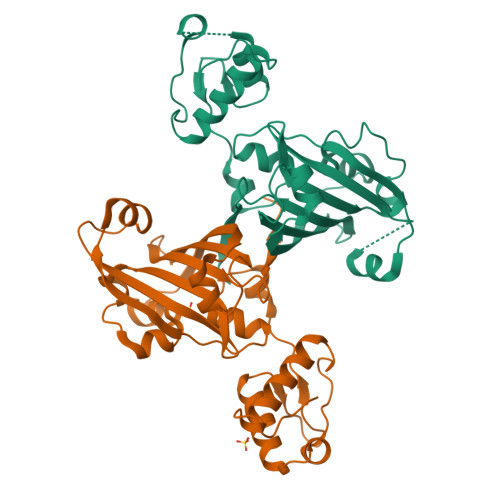
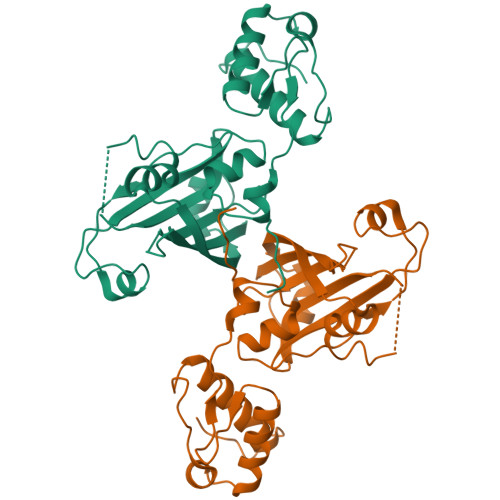
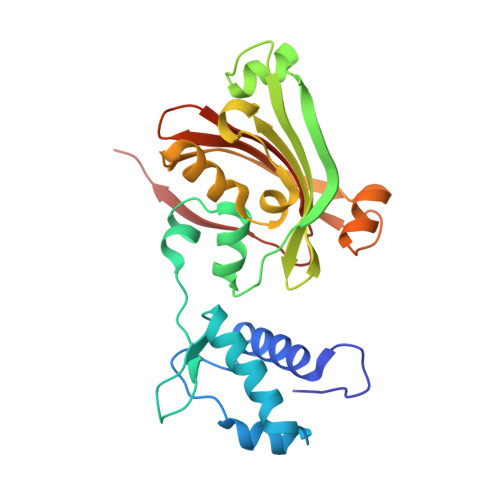
YvoA is a GntR/HutC transcription regulator from Bacillus subtilis implicated in the regulation of genes from the N-acetylglucosamine-degrading pathway. Its 2.4-A crystal structure reveals a homodimeric assembly with each monomer displaying a two-domain fold. The C-terminal domain, which binds the effector N-acetylglucosamine-6-phosphate, adopts a chorismate lyase fold, whereas the N-terminal domain contains a winged helix-turn-helix DNA-binding domain. Isothermal titration calorimetry and site-directed mutagenesis revealed that the effector-binding site in YvoA coincides with the active site of related chorismate lyase from Escherichia coli. The characterization of the DNA- and effector-binding properties of two disulfide-bridged mutants that lock YvoA in two distinct conformational states provides for the first time detailed insight into the allosteric mechanism through which effector binding modulates DNA binding and, thereby regulates transcription in a representative GntR/HutC family member. Central to this allosteric coupling mechanism is a loop-to-helix transition with the dipole of the newly formed helix pointing toward the phosphate of the effector. This transition goes in hand with the emergence of internal symmetry in the effector-binding domain and, in addition, leads to a 122 degrees rotation of the DNA-binding domains that is best described as a jumping-jack-like motion.
Organizational Affiliation:
Lehrstuhl für Biotechnik, Department of Biology, Friedrich-Alexander University Erlangen-Nuremberg, D-91052 Erlangen, Germany.