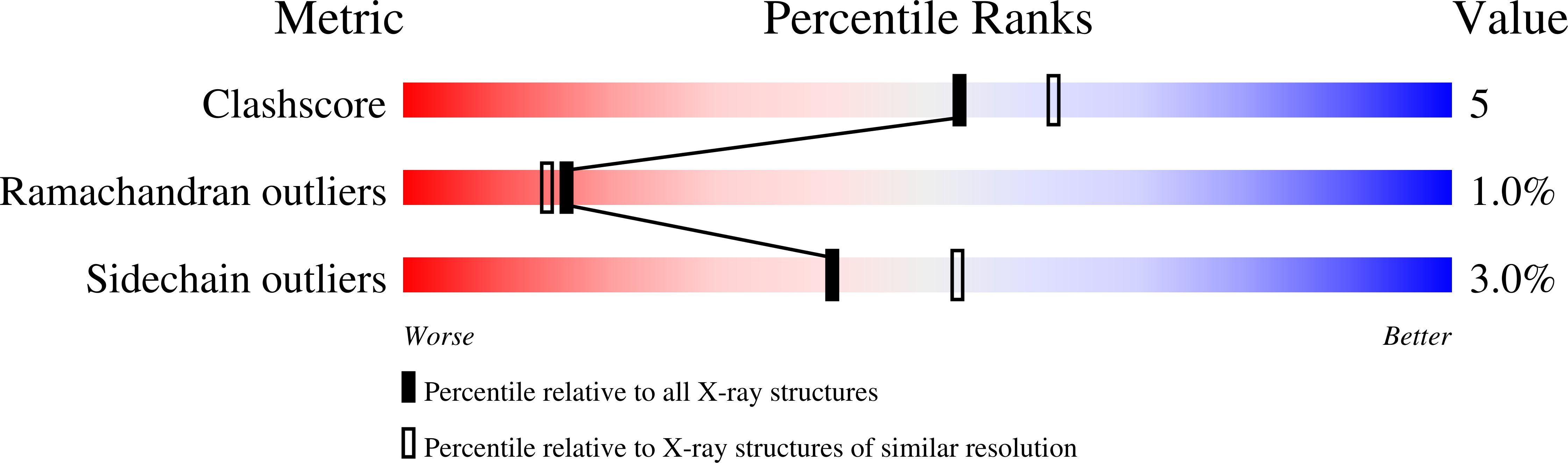Hydrogen location in stages of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction: time-of-flight neutron structure of D-xylose isomerase with bound D-xylulose
Kovalevsky, A.Y., Katz, A.K., Carrell, H.L., Hanson, L., Mustyakimov, M., Fisher, S.Z., Coates, L., Schoenborn, B.P., Bunick, G.J., Glusker, J.P., Langan, P.(2008) Biochemistry 47: 7595-7597
- PubMed: 18578508
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi8005434
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3CWH - PubMed Abstract:
The time-of-flight neutron Laue technique has been used to determine the location of hydrogen atoms in the enzyme d-xylose isomerase (XI). The neutron structure of crystalline XI with bound product, d-xylulose, shows, unexpectedly, that O5 of d-xylulose is not protonated but is hydrogen-bonded to doubly protonated His54. Also, Lys289, which is neutral in native XI, is protonated (positively charged), while the catalytic water in native XI has become activated to a hydroxyl anion which is in the proximity of C1 and C2, the molecular site of isomerization of xylose. These findings impact our understanding of the reaction mechanism.
Organizational Affiliation:
M888, Bioscience Division, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico 87545, USA.