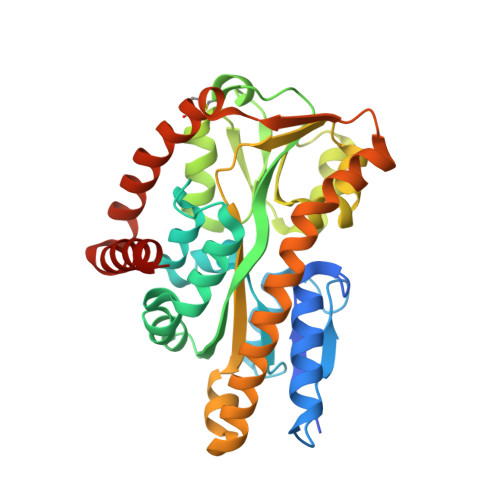
The crystal structure of UehA in complex with ectoine-A comparison with other TRAP-T binding proteins.
Lecher, J., Pittelkow, M., Zobel, S., Bursy, J., Bonig, T., Smits, S.H., Schmitt, L., Bremer, E.(2009) J Mol Biol 389: 58-73
- PubMed: 19362561
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2009.03.077
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3FXB - PubMed Abstract:
Substrate-binding proteins or extracellular solute receptors (ESRs) are components of both ABC (ATP binding cassette) and TRAP-T (tripartite ATP-independent periplasmic transporter). The TRAP-T system UehABC from Silicibacter pomeroyi DSS-3 imports the compatible solutes ectoine and 5-hydroxyectoine as nutrients. UehA, the ESR of the UehABC operon, binds both ectoine and 5-hydroxyectoine with high affinity (K(d) values of 1.4+/-0.1 and 1.1+/-0.1 microM, respectively) and delivers them to the TRAP-T complex. The crystal structure of UehA in complex with ectoine was determined at 2.9-A resolution and revealed an overall fold common for all ESR proteins from TRAP systems determined so far. A comparison of the recently described structure of TeaA from Halomonas elongata and an ectoine-binding protein (EhuB) from an ABC transporter revealed a conserved ligand binding mode that involves both directed and cation-pi interactions. Furthermore, a comparison with other known TRAP-T ESRs revealed a helix that might act as a selectivity filter imposing restraints on the ESRs that fine-tune ligand recognition and binding and finally might determine the selection of the cognate substrate.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Biochemistry, Heinrich-Heine-University Duesseldorf, Germany.