Crystal Structures of Glycoside Hydrolase Family 51 alpha-L-Arabinofuranosidase from Thermotoga maritima
Im, D.-H., Kimura, K.I., Hayasaka, F., Tanaka, T., Noguchi, M., Kobayashi, A., Shoda, S., Miyazaki, K., Wakagi, T., Fushinobu, S.(2012) Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 76: 423-428
- PubMed: 22313787
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.110902
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3UG3, 3UG4, 3UG5 - PubMed Abstract:
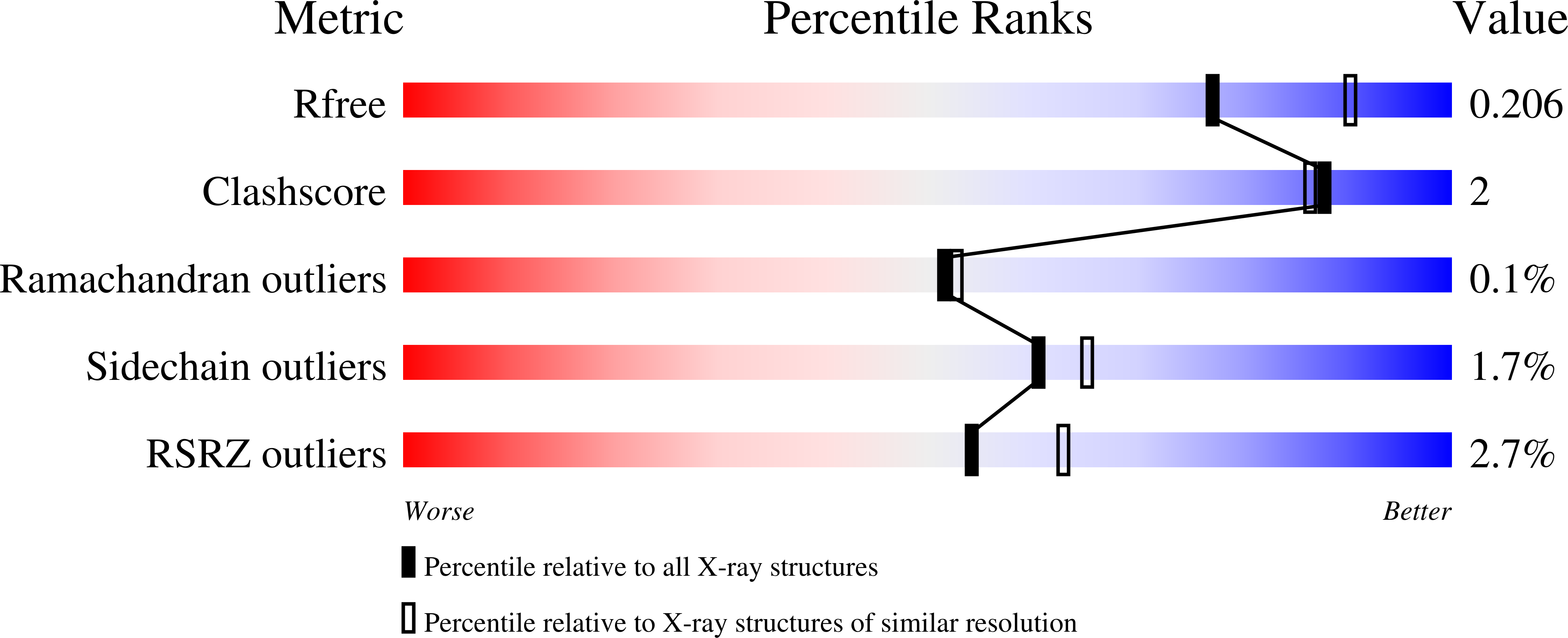
α-L-Arabinofuranosidase from the hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga maritima (Tm-AFase) is an extremely thermophilic enzyme belonging to glycoside hydrolase family 51. It can catalyze the transglycosylation of a novel glycosyl donor, 4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl (DMT)-β-D-xylopyranoside. In this study we determined the crystal structures of Tm-AFase in substrate-free and complex forms with arabinose and xylose at 1.8-2.3 Å resolution to determine the architecture of the substrate binding pocket. Subsite -1 of Tm-AFase is similar to that of α-L-arabinofuranosidase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus, but the substrate binding pocket of Tm-AFase is narrower and more hydrophobic. Possible substrate binding modes were investigated by automated docking analysis.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biotechnology, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan.