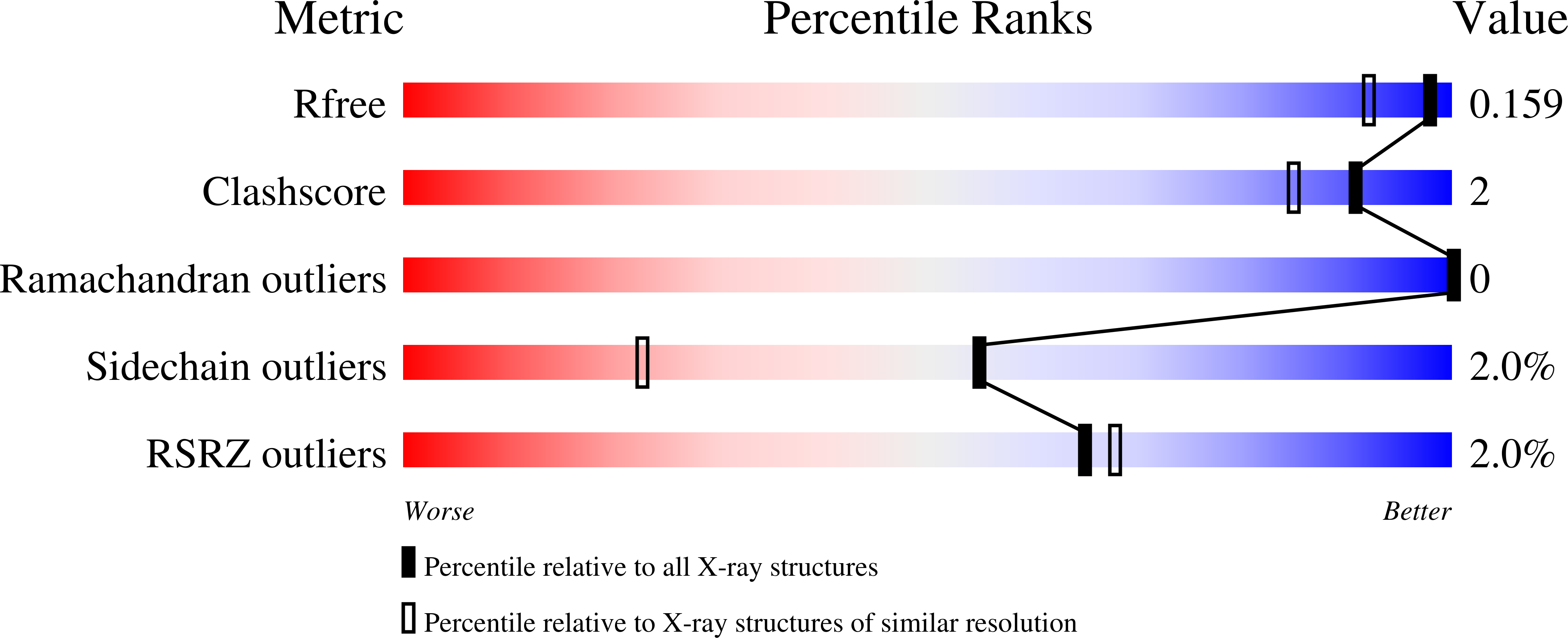
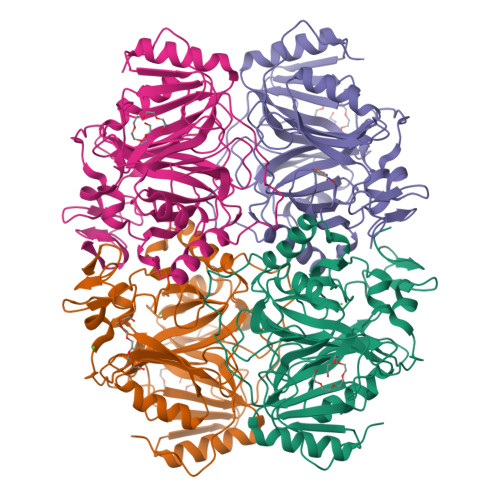
Structural Basis for Substrate and Oxygen Activation in Homoprotocatechuate 2,3-Dioxygenase: Roles of Conserved Active Site Histidine 200.
Kovaleva, E.G., Rogers, M.S., Lipscomb, J.D.(2015) Biochemistry 54: 5329-5339
- PubMed: 26267790
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00709
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4Z6L, 4Z6M, 4Z6N, 4Z6O, 4Z6P, 4Z6Q, 4Z6R, 4Z6S, 4Z6T, 4Z6U, 4Z6V, 4Z6W, 4Z6Z - PubMed Abstract:
Kinetic and spectroscopic studies have shown that the conserved active site residue His200 of the extradiol ring-cleaving homoprotocatechuate 2,3-dioxygenase (FeHPCD) from Brevibacterium fuscum is critical for efficient catalysis. The roles played by this residue are probed here by analysis of the steady-state kinetics, pH dependence, and X-ray crystal structures of the FeHPCD position 200 variants His200Asn, His200Gln, and His200Glu alone and in complex with three catecholic substrates (homoprotocatechuate, 4-sulfonylcatechol, and 4-nitrocatechol) possessing substituents with different inductive capacity. Structures determined at 1.35-1.75 Å resolution show that there is essentially no change in overall active site architecture or substrate binding mode for these variants when compared to the structures of the wild-type enzyme and its analogous complexes. This shows that the maximal 50-fold decrease in kcat for ring cleavage, the dramatic changes in pH dependence, and the switch from ring cleavage to ring oxidation of 4-nitrocatechol by the FeHPCD variants can be attributed specifically to the properties of the altered second-sphere residue and the substrate. The results suggest that proton transfer is necessary for catalysis, and that it occurs most efficiently when the substrate provides the proton and His200 serves as a catalyst. However, in the absence of an available substrate proton, a defined proton-transfer pathway in the protein can be utilized. Changes in the steric bulk and charge of the residue at position 200 appear to be capable of altering the rate-limiting step in catalysis and, perhaps, the nature of the reactive species.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biology, University of Leeds , Leeds LS2 9JT, U.K.