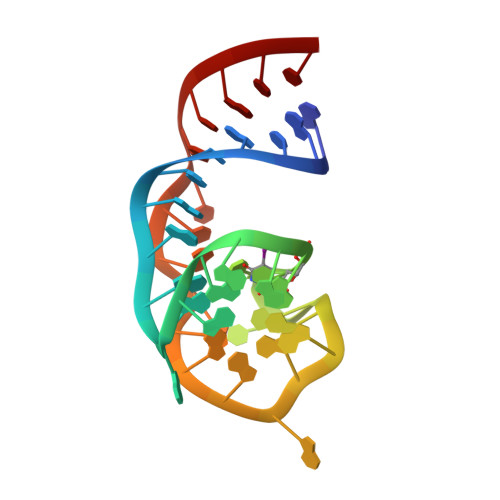
A homodimer interface without base pairs in an RNA mimic of red fluorescent protein.
Warner, K.D., Sjekloca, L., Song, W., Filonov, G.S., Jaffrey, S.R., Ferre-D'Amare, A.R.(2017) Nat Chem Biol 13: 1195-1201
- PubMed: 28945234
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.2475
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5BJO, 5BJP - PubMed Abstract:
Corn, a 28-nucleotide RNA, increases yellow fluorescence of its cognate ligand 3,5-difluoro-4-hydroxybenzylidene-imidazolinone-2-oxime (DFHO) by >400-fold. Corn was selected in vitro to overcome limitations of other fluorogenic RNAs, particularly rapid photobleaching. We now report the Corn-DFHO co-crystal structure, discovering that the functional species is a quasisymmetric homodimer. Unusually, the dimer interface, in which six unpaired adenosines break overall two-fold symmetry, lacks any intermolecular base pairs. The homodimer encapsulates one DFHO at its interprotomer interface, sandwiching it with a G-quadruplex from each protomer. Corn and the green-fluorescent Spinach RNA are structurally unrelated. Their convergent use of G-quadruplexes underscores the usefulness of this motif for RNA-induced small-molecule fluorescence. The asymmetric dimer interface of Corn could provide a basis for the development of mutants that only fluoresce as heterodimers. Such variants would be analogous to Split GFP, and may be useful for analyzing RNA co-expression or association, or for designing self-assembling RNA nanostructures.
Organizational Affiliation:
Biochemistry and Biophysics Center, National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute, Bethesda, Maryland, USA.