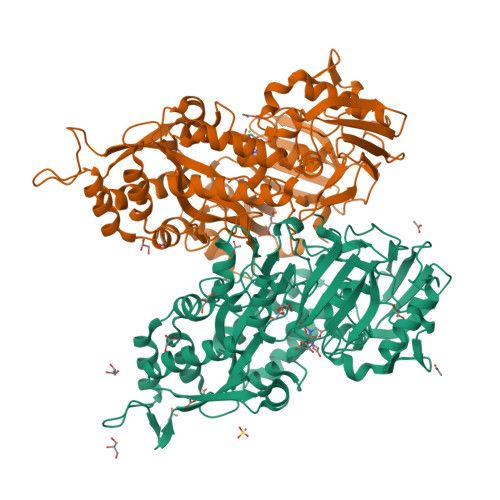
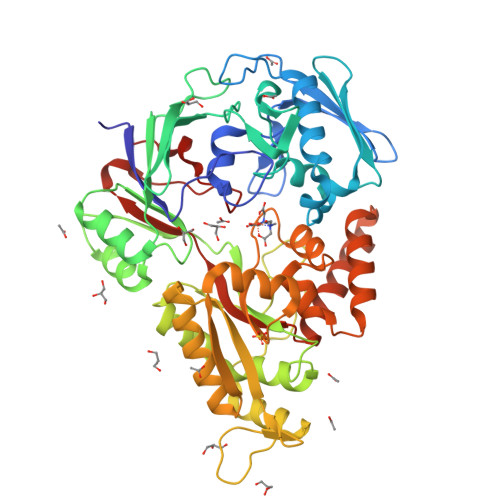
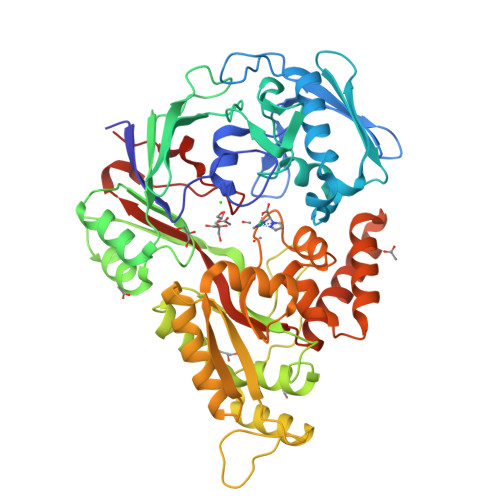
Efficient conversion of alkenes to chlorohydrins by a Ru-based artificial enzyme.
Lopez, S., Rondot, L., Cavazza, C., Iannello, M., Boeri-Erba, E., Burzlaff, N., Strinitz, F., Jorge-Robin, A., Marchi-Delapierre, C., Menage, S.(2017) Chem Commun (Camb) 53: 3579-3582
- PubMed: 28289745
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c6cc08873b
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5L8D - PubMed Abstract:
Artificial enzymes are required to catalyse non-natural reactions. Here, a hybrid catalyst was developed by embedding a novel Ru complex in the transport protein NikA. The protein scaffold activates the bound Ru complex to produce a catalyst with high regio- and stereo-selectivity. The hybrid efficiently and stably produced α-hydroxy-β-chloro chlorohydrins from alkenes (up to 180 TON with a TOF of 1050 h -1 ).
Organizational Affiliation:
Université Grenoble Alpes, Laboratoire de Chimie et Biologie des Métaux, BioCE, F-Grenoble, France and CNRS, Laboratoire de Chimie et Biologie des Métaux, BioCat, UMR 5249, France and CEA-Grenoble, DRF/BIG/CBM, F-Grenoble, France. stephane.menage@cea.fr.