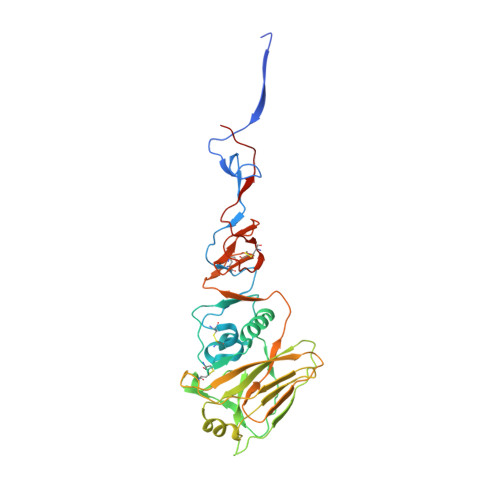
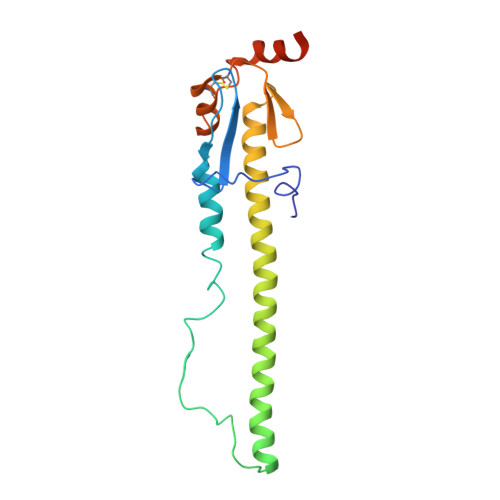
Assessment of Molecular, Antigenic, and Pathological Features of Canine Influenza A(H3N2) Viruses That Emerged in the United States.
Pulit-Penaloza, J.A., Simpson, N., Yang, H., Creager, H.M., Jones, J., Carney, P., Belser, J.A., Yang, G., Chang, J., Zeng, H., Thor, S., Jang, Y., Killian, M.L., Jenkins-Moore, M., Janas-Martindale, A., Dubovi, E., Wentworth, D.E., Stevens, J., Tumpey, T.M., Davis, C.T., Maines, T.R.(2017) J Infect Dis 216: S499-S507
- PubMed: 28934454
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiw620
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6N4D, 6N4F - PubMed Abstract:
A single subtype of canine influenza virus (CIV), A(H3N8), was circulating in the United States until a new subtype, A(H3N2), was detected in Illinois in spring 2015. Since then, this CIV has caused thousands of infections in dogs in multiple states. In this study, genetic and antigenic properties of the new CIV were evaluated. In addition, structural and glycan array binding features of the recombinant hemagglutinin were determined. Replication kinetics in human airway cells and pathogenesis and transmissibility in animal models were also assessed. A(H3N2) CIVs maintained molecular and antigenic features related to low pathogenicity avian influenza A(H3N2) viruses and were distinct from A(H3N8) CIVs. The structural and glycan array binding profile confirmed these findings and revealed avian-like receptor-binding specificity. While replication kinetics in human airway epithelial cells was on par with that of seasonal influenza viruses, mild-to-moderate disease was observed in infected mice and ferrets, and the virus was inefficiently transmitted among cohoused ferrets. Further adaptation is needed for A(H3N2) CIVs to present a likely threat to humans. However, the potential for coinfection of dogs and possible reassortment of human and other animal influenza A viruses presents an ongoing risk to public health.
- Influenza Division, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia.
Organizational Affiliation: