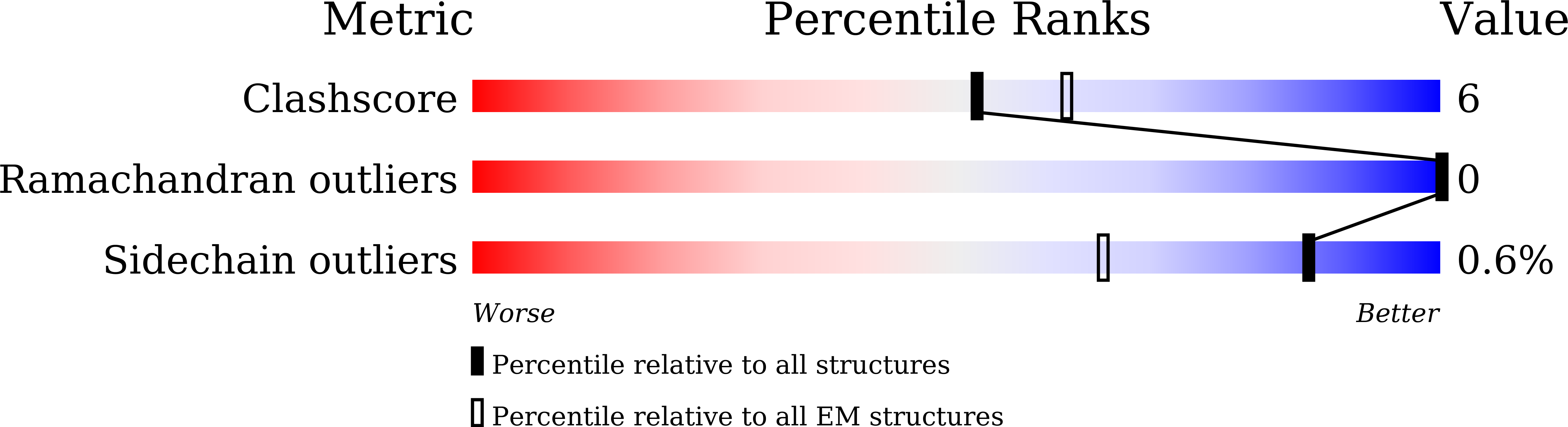Somatically hypermutated antibodies isolated from SARS-CoV-2 Delta infected patients cross-neutralize heterologous variants.
Yu, H., Liu, B., Zhang, Y., Gao, X., Wang, Q., Xiang, H., Peng, X., Xie, C., Wang, Y., Hu, P., Shi, J., Shi, Q., Zheng, P., Feng, C., Tang, G., Liu, X., Guo, L., Lin, X., Li, J., Liu, C., Huang, Y., Yang, N., Chen, Q., Li, Z., Su, M., Yan, Q., Pei, R., Chen, X., Liu, L., Hu, F., Liang, D., Ke, B., Ke, C., Li, F., He, J., Wang, M., Chen, L., Xiong, X., Tang, X.(2023) Nat Commun 14: 1058-1058
- PubMed: 36828833
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-36761-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8HC2, 8HC3, 8HC4, 8HC5, 8HC6, 8HC7, 8HC8, 8HC9, 8HCA, 8HCB - PubMed Abstract:
SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants feature highly mutated spike proteins with extraordinary abilities in evading antibodies isolated earlier in the pandemic. Investigation of memory B cells from patients primarily with breakthrough infections with the Delta variant enables isolation of a number of neutralizing antibodies cross-reactive to heterologous variants of concern (VOCs) including Omicron variants (BA.1-BA.4). Structural studies identify altered complementarity determining region (CDR) amino acids and highly unusual heavy chain CDR2 insertions respectively in two representative cross-neutralizing antibodies-YB9-258 and YB13-292. These features are putatively introduced by somatic hypermutation and they are heavily involved in epitope recognition to broaden neutralization breadth. Previously, insertions/deletions were rarely reported for antiviral antibodies except for those induced by HIV-1 chronic infections. These data provide molecular mechanisms for cross-neutralization of heterologous SARS-CoV-2 variants by antibodies isolated from Delta variant infected patients with implications for future vaccination strategy.
Organizational Affiliation:
Guangzhou Eighth People's Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China. yuhaisheng@gzhmu.edu.cn.