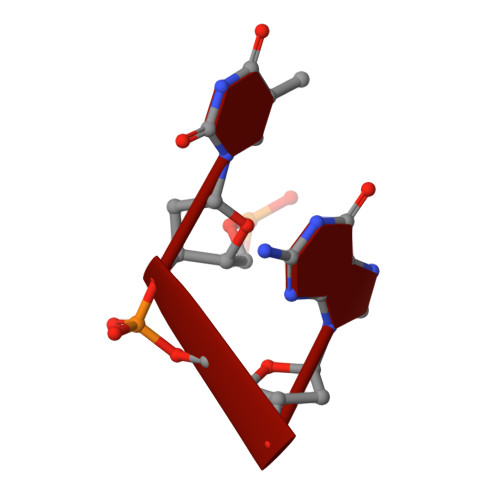
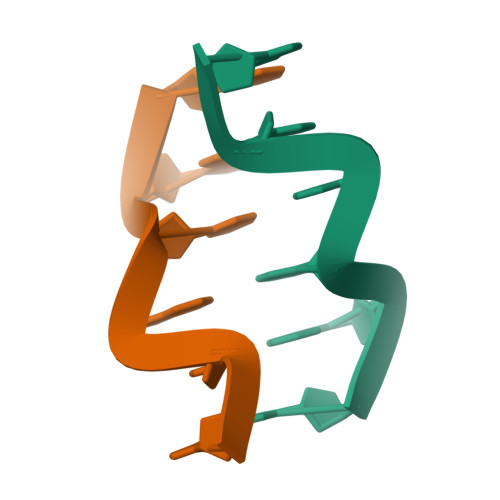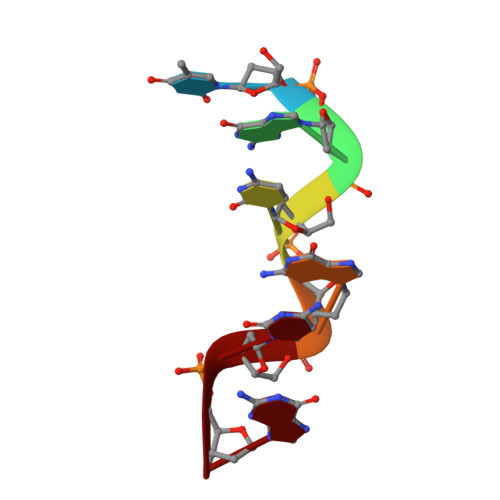Cobalt hexammine induced tautomeric shift in Z-DNA: the structure of d(CGCGCA)*d(TGCGCG) in two crystal forms.
Thiyagarajan, S., Rajan, S.S., Gautham, N.(2004) Nucleic Acids Res 32: 5945-5953
- PubMed: 15534365
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh919
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1XA2, 1XAM - PubMed Abstract:
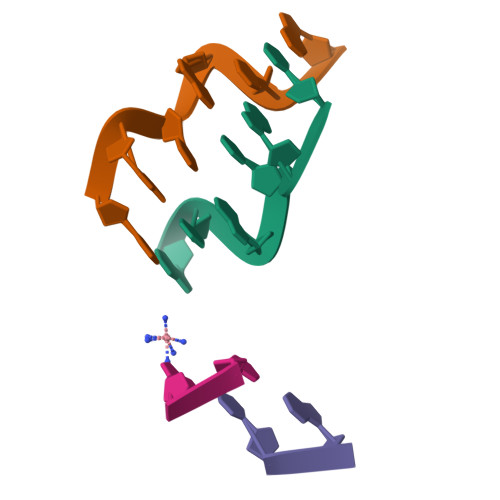
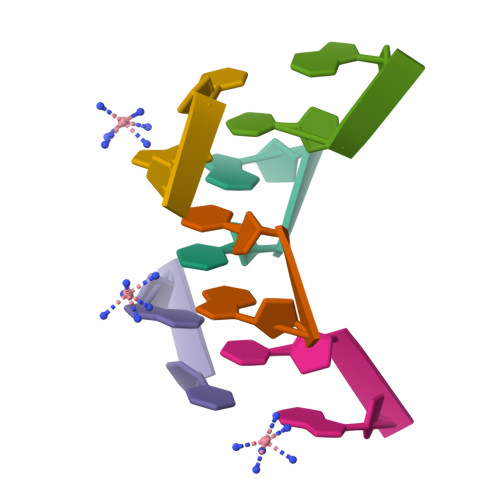
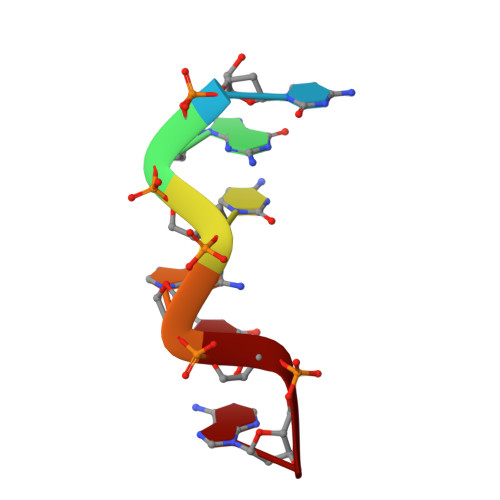
We report here the crystal structure of the DNA hexamer duplex d(CGCGCA)*d(TGCGCG) at 1.71 A resolution. The crystals, in orthorhombic space group, were grown in the presence of cobalt hexammine, a known inducer of the left-handed Z form of DNA. The interaction of this ion with the DNA helix results in a change of the adenine base from the common amino tautomeric form to the imino tautomer. Consequently the A:T base pair is disrupted from the normal Watson-Crick base pairing to a 'wobble' like base pairing. This change is accommodated easily within the helix, and the helical parameters are those expected for Z-DNA. When the cobalt hexammine concentration is decreased slightly in the crystallization conditions, the duplex crystallizes in a different, hexagonal space group, with two hexamer duplexes in the asymmetric unit. One of these is situated on a crystallographic 6-fold screw axis, leading to disorder. The tautomeric shift is not observed in this space group. We show that the change in inter-helix interactions that lead to the two different space groups probably arise from the small decrease in ion concentration, and consequently disordered positions for the ion.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Crystallography and Biophysics, University of Madras, Guindy Campus, Chennai 600 025, India.