Structural basis for LeishIF4E-1 modulation by an interacting protein in the human parasite Leishmania major.
Meleppattu, S., Arthanari, H., Zinoviev, A., Boeszoermenyi, A., Wagner, G., Shapira, M., Leger-Abraham, M.(2018) Nucleic Acids Res 46: 3791-3801
- PubMed: 29562352
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky194
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5WB5 - PubMed Abstract:
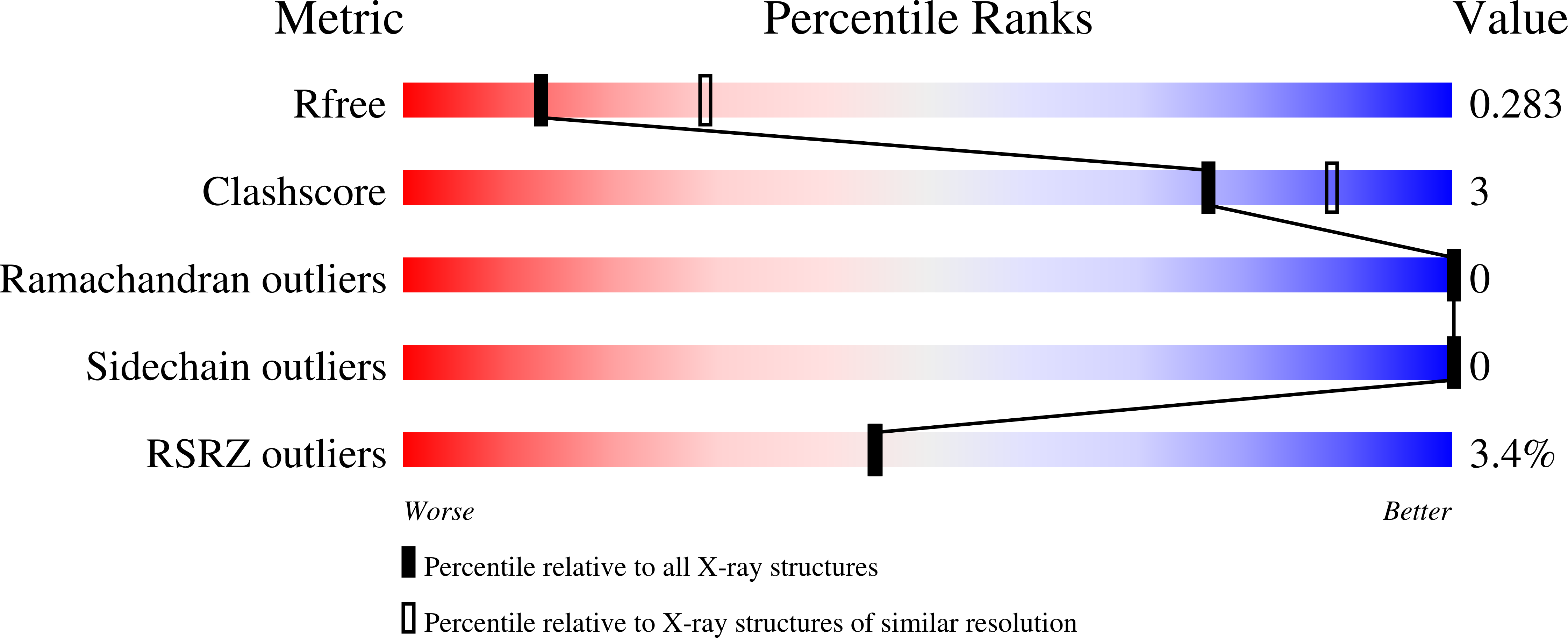
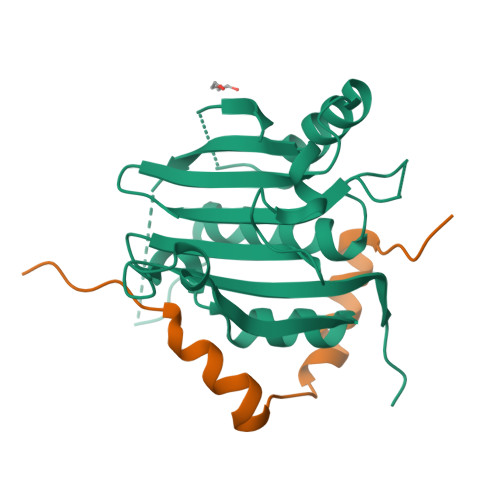
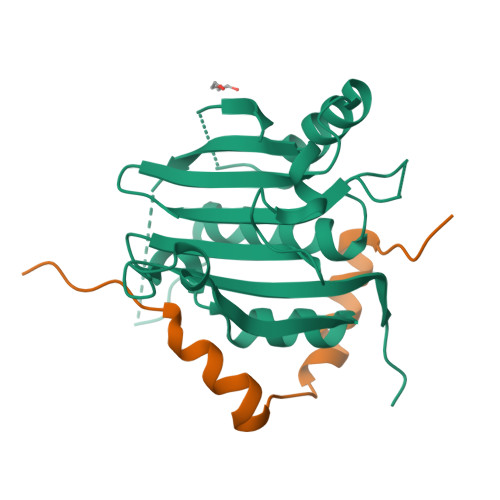
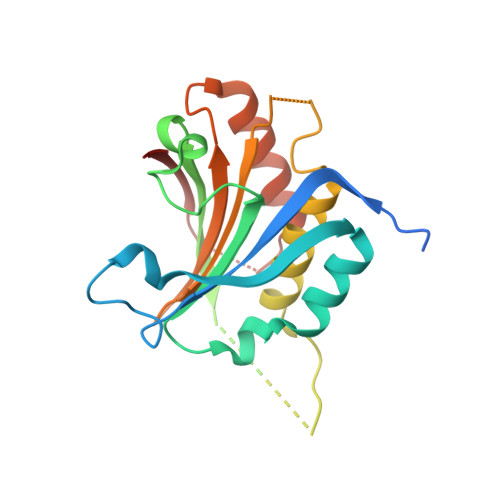
Leishmania parasites are unicellular pathogens that are transmitted to humans through the bite of infected sandflies. Most of the regulation of their gene expression occurs post-transcriptionally, and the different patterns of gene expression required throughout the parasites' life cycle are regulated at the level of translation. Here, we report the X-ray crystal structure of the Leishmania cap-binding isoform 1, LeishIF4E-1, bound to a protein fragment of previously unknown function, Leish4E-IP1, that binds tightly to LeishIF4E-1. The molecular structure, coupled to NMR spectroscopy experiments and in vitro cap-binding assays, reveal that Leish4E-IP1 allosterically destabilizes the binding of LeishIF4E-1 to the 5' mRNA cap. We propose mechanisms through which Leish4E-IP1-mediated LeishIF4E-1 inhibition could regulate translation initiation in the human parasite.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Microbiology and Immunobiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115, USA.