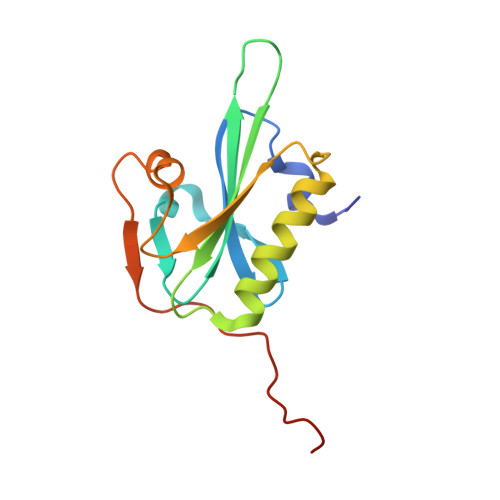
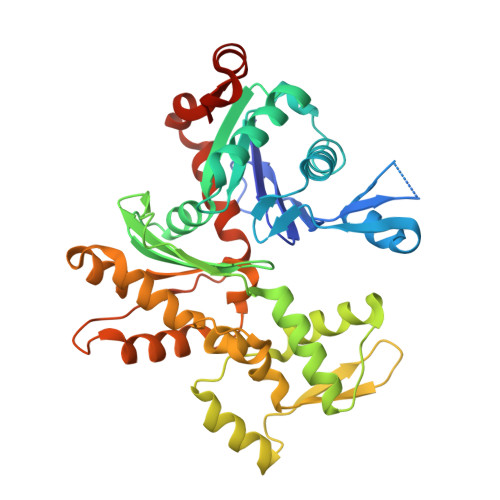
From the First to the second domain of gelsolin: A common path on the surface of actin?
Irobi, E., Burtnick, L.D., Urosev, D., Narayan, K., Robinson, R.C.(2003) FEBS Lett 552: 86-90
- PubMed: 14527665
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00934-7
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1P8Z - PubMed Abstract:
We present the 2.6 A resolution crystal structure of a complex formed between G-actin and gelsolin fragment Met25-Gln160 (G1+). The structure differs from those of other gelsolin domain 1 (G1) complexes in that an additional six amino acid residues from the crucial linker region into gelsolin domain 2 (G2) are visible and are attached securely to the surface of actin. The linker segment extends away from G1 up the face of actin in a direction that infers G2 will bind along the same long-pitch helical strand as the actin bound to G1. This is consistent with a mechanism whereby G2 attaches gelsolin to the side of a filament and then directs G1 toward a position where it would disrupt actin-actin contacts. Alignment of the sequence of the structurally important residues within the G1-G2 linker with those of WH2 (WASp homology domain 2) domain protein family members (e.g. WASp (Wiscott-Aldridge syndrome protein) and thymosin beta4) suggests that the opposing activities of filament assembly and disassembly may exploit a common patch on the surface of actin.
- Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology, Uppsala University, Box 582, 751 23 Uppsala, Sweden.
Organizational Affiliation: