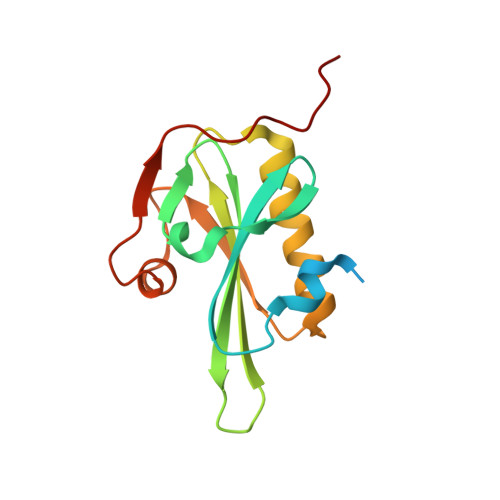
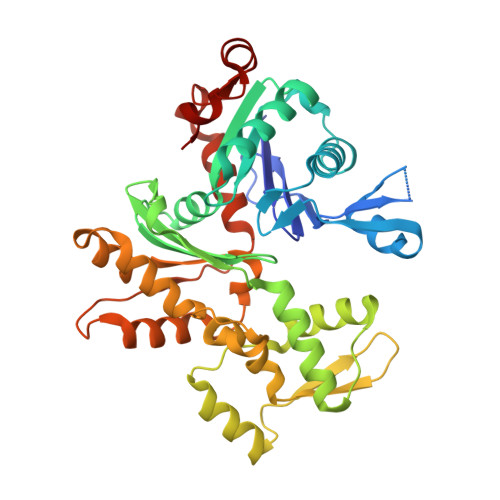
The Structural Basis of Actin Interaction with Multiple WH2/beta-Thymosin Motif-Containing Proteins
Aguda, A.H., Xue, B., Irobi, E., Preat, T., Robinson, R.C.(2006) Structure 14: 469-476
- PubMed: 16531231
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2005.12.011
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2FF3, 2FF6 - PubMed Abstract:
Participation of actin in cellular processes relies on the dynamics of filament assembly. Filament elongation is fed by monomeric actin in complex with either profilin or a Wiscott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) homology domain 2 (WH2)/beta-thymosin (betaT) domain. WH2/betaT motif repetition (typified by ciboulot) or combination with nonrelated domains (as found in N-WASP) results in proteins that yield their actin to filament elongation. Here, we report the crystal structures of actin bound hybrid proteins, constructed between gelsolin and WH2/betaT domains from ciboulot or N-WASP. We observe the C-terminal half of ciboulot domain 2 bound to actin. In solution, we show that cibolout domains 2 and 3 bind to both G- and F-actin, and that whole ciboulot forms a complex with two actin monomers. In contrast, the analogous portion of N-WASP WH2 domain 2 is detached from actin, indicating that the C-terminal halves of the betaT and WH2 motifs are not functionally analogous.
- Department of Medical Biochemistry and Microbiology, Uppsala Biomedical Center, Uppsala University, Uppsala 751 23, Sweden.
Organizational Affiliation: