Asparaginyl hydroxylation of the Notch ankyrin repeat domain by factor inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor.
Coleman, M.L., McDonough, M.A., Hewitson, K.S., Coles, C., Mecinovic, J., Edelmann, M., Cook, K.M., Cockman, M.E., Lancaster, D.E., Kessler, B.M., Oldham, N.J., Ratcliffe, P.J., Schofield, C.J.(2007) J Biol Chem 282: 24027-24038
- PubMed: 17573339
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M704102200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
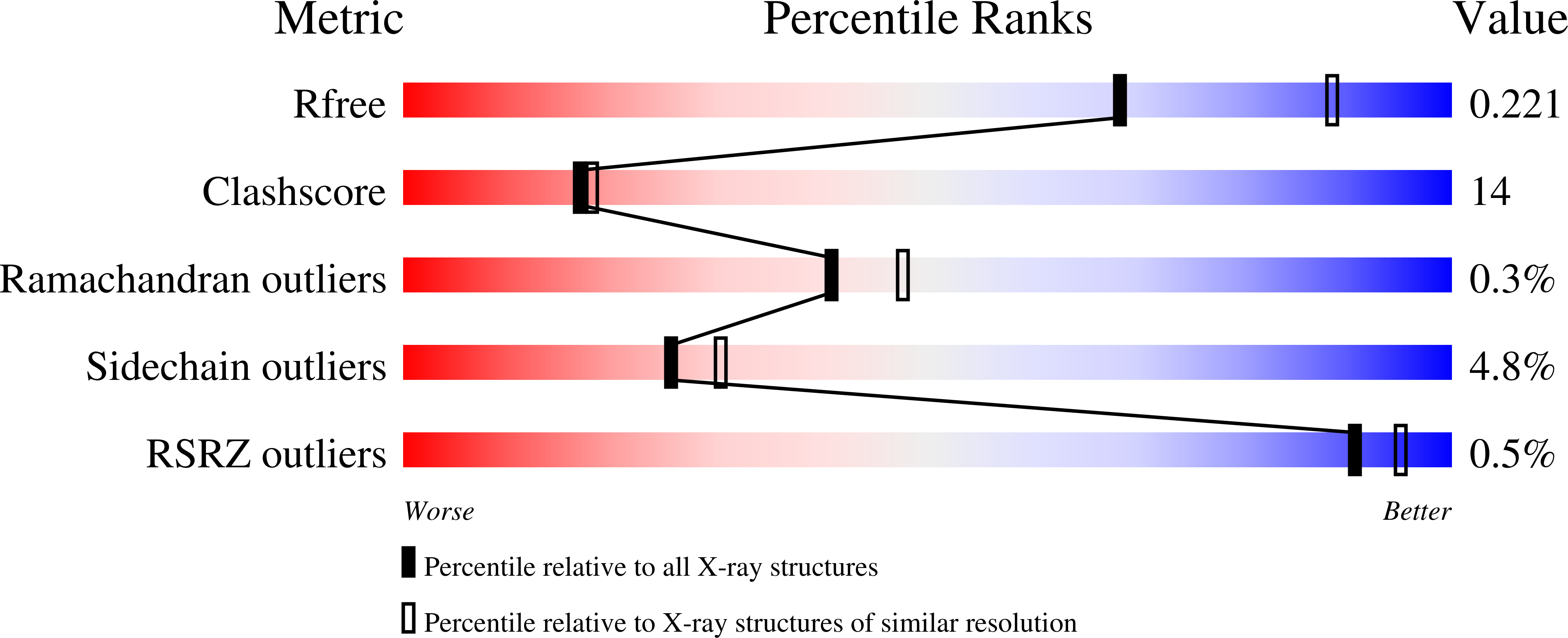
2QC9, 3P3N, 3P3P - PubMed Abstract:
The stability and activity of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) are regulated by the post-translational hydroxylation of specific prolyl and asparaginyl residues. We show that the HIF asparaginyl hydroxylase, factor inhibiting HIF (FIH), also catalyzes hydroxylation of highly conserved asparaginyl residues within ankyrin repeat (AR) domains (ARDs) of endogenous Notch receptors. AR hydroxylation decreases the extent of ARD binding to FIH while not affecting signaling through the canonical Notch pathway. ARD proteins were found to efficiently compete with HIF for FIH-dependent hydroxylation. Crystallographic analyses of the hydroxylated Notch ARD (2.35A) and of Notch peptides bound to FIH (2.4-2.6A) reveal the stereochemistry of hydroxylation on the AR and imply that significant conformational changes are required in the ARD fold in order to enable hydroxylation at the FIH active site. We propose that ARD proteins function as natural inhibitors of FIH and that the hydroxylation status of these proteins provides another oxygen-dependent interface that modulates HIF signaling.
Organizational Affiliation:
Henry Wellcome Building for Molecular Physiology, University of Oxford, Oxford, OX3 7BN, United Kingdom.