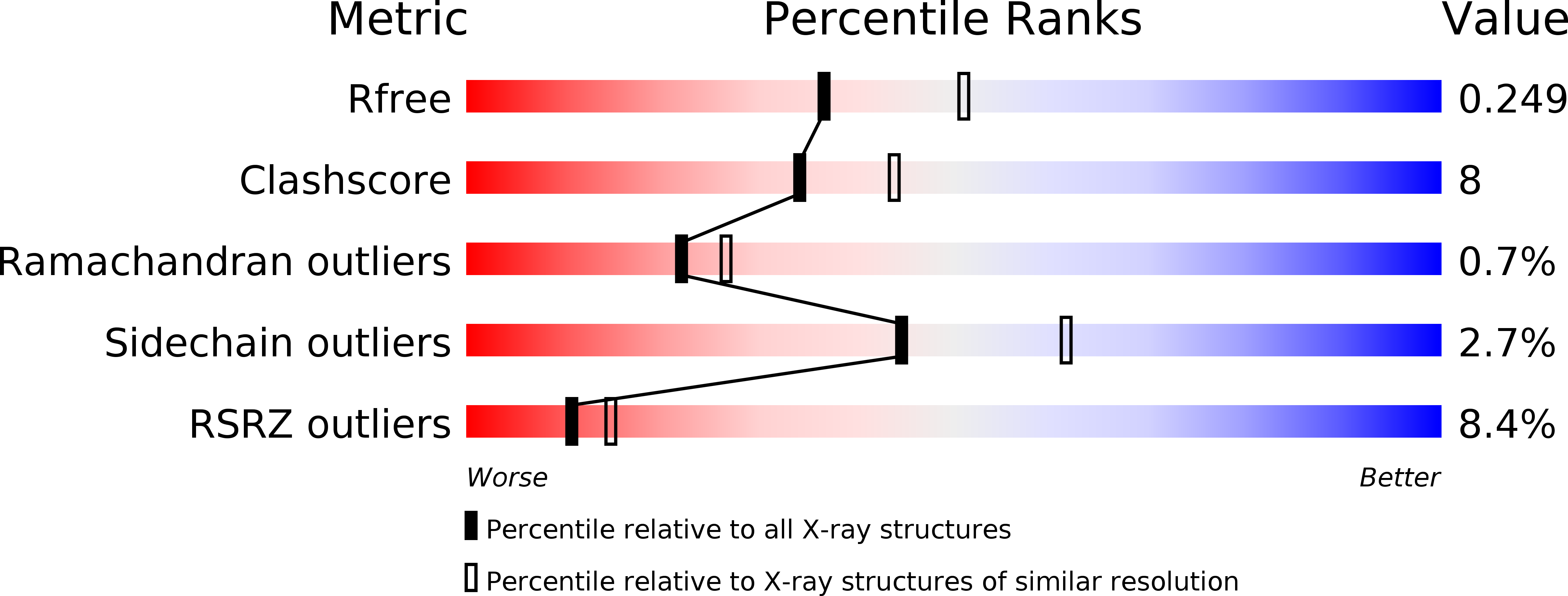
Structural basis for selective inhibition of purine nucleoside phosphorylase from Schistosoma mansoni: kinetic and structural studies.
Castilho, M.S., Postigo, M.P., Pereira, H.M., Oliva, G., Andricopulo, A.D.(2010) Bioorg Med Chem 18: 1421-1427
- PubMed: 20129792
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2010.01.022
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3DJF, 3IEX - PubMed Abstract:
Selectivity plays a crucial role in the design of enzyme inhibitors as novel antiparasitic agents, particularly in cases where the target enzyme is also present in the human host. Purine nucleoside phosphorylase from Schistosoma mansoni (SmPNP) is an attractive target for the discovery of potential antischistosomal agents. In the present work, kinetic studies were carried out in order to determine the inhibitory potency, mode of action and enzyme selectivity of a series of inhibitors of SmPNP. In addition, crystallographic studies provided important structural insights for rational inhibitor design, revealing consistent structural differences in the binding mode of the inhibitors in the active sites of the SmPNP and human PNP (HsPNP) structures. The molecular information gathered in this work should be useful for future medicinal chemistry efforts in the design of new inhibitors of SmPNP having increased affinity and selectivity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Universidade Federal da Bahia, Faculdade de Farmácia, R. Barão de Jeremoabo, Salvador-BA, Brazil. castilho@ufba.br