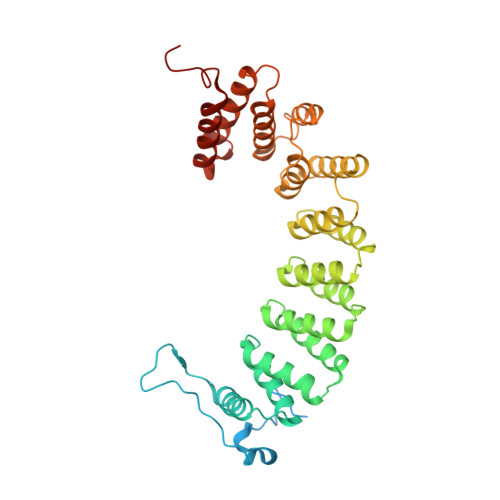
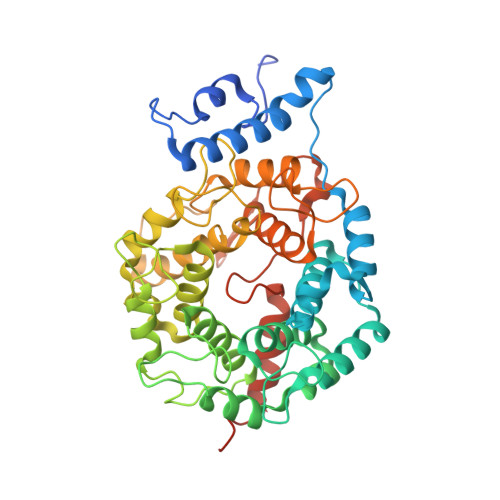
Caged protein prenyltransferase substrates: tools for understanding protein prenylation.
DeGraw, A.J., Hast, M.A., Xu, J., Mullen, D., Beese, L.S., Barany, G., Distefano, M.D.(2008) Chem Biol Drug Des 72: 171-181
- PubMed: 18844669
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-0285.2008.00698.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3DPY - PubMed Abstract:
Originally designed to block the prenylation of oncogenic Ras, inhibitors of protein farnesyltransferase currently in preclinical and clinical trials are showing efficacy in cancers with normal Ras. Blocking protein prenylation has also shown promise in the treatment of malaria, Chagas disease and progeria syndrome. A better understanding of the mechanism, targets and in vivo consequences of protein prenylation are needed to elucidate the mode of action of current PFTase (Protein Farnesyltransferase) inhibitors and to create more potent and selective compounds. Caged enzyme substrates are useful tools for understanding enzyme mechanism and biological function. Reported here is the synthesis and characterization of caged substrates of PFTase. The caged isoprenoid diphosphates are poor substrates prior to photolysis. The caged CAAX peptide is a true catalytically caged substrate of PFTase in that it is to not a substrate, yet is able to bind to the enzyme as established by inhibition studies and X-ray crystallography. Irradiation of the caged molecules with 350 nm light readily releases their cognate substrate and their photolysis products are benign. These properties highlight the utility of those analogs towards a variety of in vitro and in vivo applications.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455, USA.