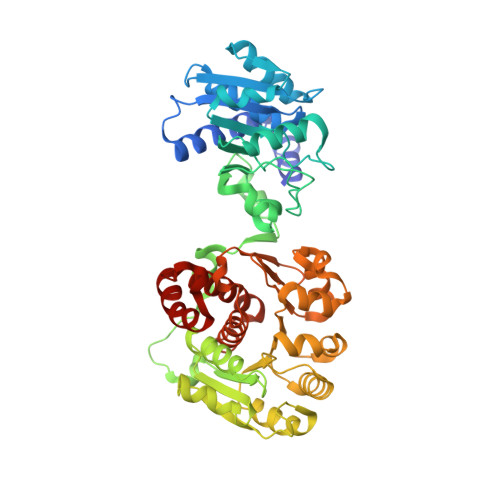
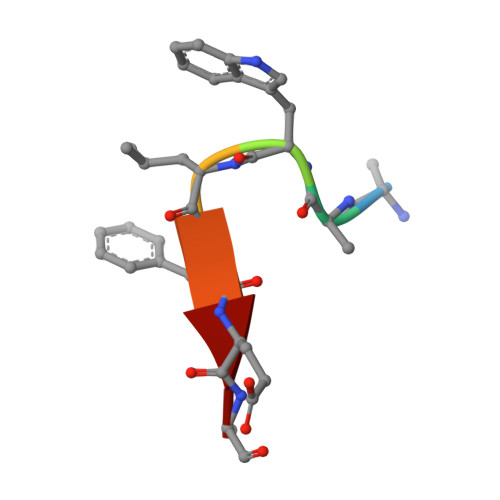
Identification of unknown protein function using metabolite cocktail screening.
Shumilin, I.A., Cymborowski, M., Chertihin, O., Jha, K.N., Herr, J.C., Lesley, S.A., Joachimiak, A., Minor, W.(2012) Structure 20: 1715-1725
- PubMed: 22940582
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2012.07.016
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3RNO, 3RO7, 3ROE, 3ROG, 3ROX, 3ROZ, 3RPH, 3RPZ, 3RQ2, 3RQ5, 3RQ6, 3RQ8, 3RQH, 3RQQ, 3RQX, 3RRB, 3RRE, 3RRF, 3RRJ, 3RS8, 3RS9, 3RSF, 3RSG, 3RSQ, 3RSS, 3RT7, 3RT9, 3RTA, 3RTB, 3RTC, 3RTD, 3RTE, 3RTG, 3RU2, 3RU3 - PubMed Abstract:
Proteins of unknown function comprise a significant fraction of sequenced genomes. Defining the roles of these proteins is vital to understanding cellular processes. Here, we describe a method to determine a protein function based on the identification of its natural ligand(s) by the crystallographic screening of the binding of a metabolite library, followed by a focused search in the metabolic space. The method was applied to two protein families with unknown function, PF01256 and YjeF_N. The PF01256 proteins, represented by YxkO from Bacillus subtilis and the C-terminal domain of Tm0922 from Thermotoga maritima, were shown to catalyze ADP/ATP-dependent NAD(P)H-hydrate dehydratation, a previously described orphan activity. The YjeF_N proteins, represented by mouse apolipoprotein A-I binding protein and the N-terminal domain of Tm0922, were found to interact with an adenosine diphosphoribose-related substrate and likely serve as ADP-ribosyltransferases. Crystallographic screening of metabolites serves as an efficient tool in functional analyses of uncharacterized proteins.
- Department of Molecular Physiology and Biological Physics, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA 22908, USA. ias2n@virginia.edu
Organizational Affiliation: