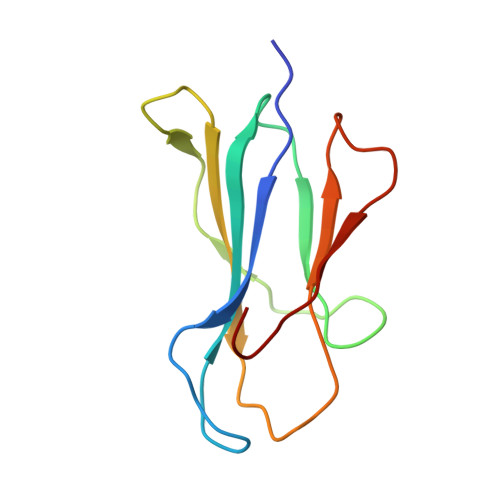
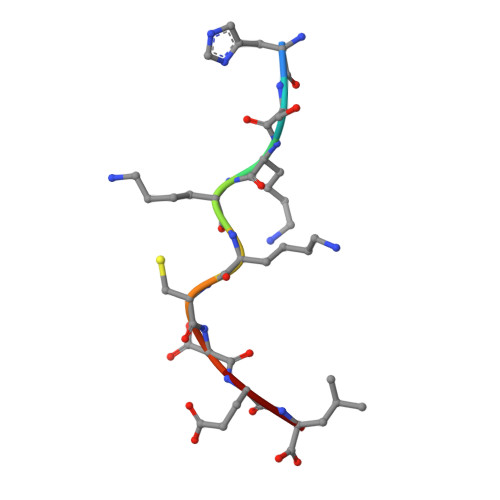
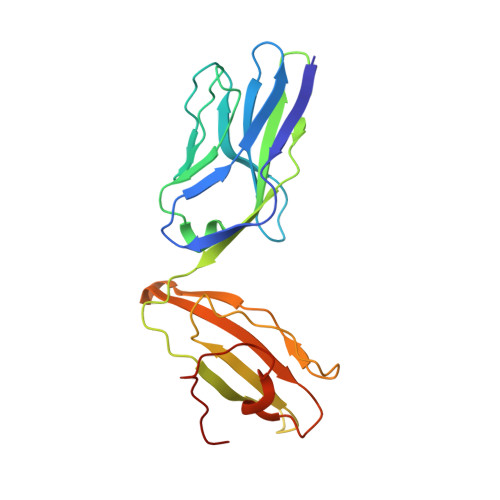
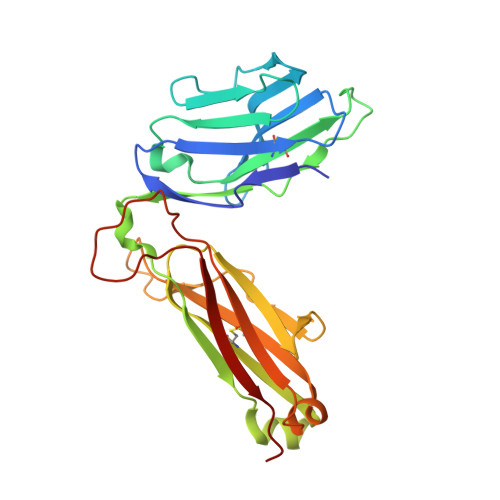
An Extensive Antigenic Footprint Underpins Immunodominant TCR Adaptability against a Hypervariable Viral Determinant.
Nivarthi, U.K., Gras, S., Kjer-Nielsen, L., Berry, R., Lucet, I.S., Miles, J.J., Tracy, S.L., Purcell, A.W., Bowden, D.S., Hellard, M., Rossjohn, J., McCluskey, J., Bharadwaj, M.(2014) J Immunol 193: 5402-5413
- PubMed: 25355921
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1401357
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4QRP, 4QRQ - PubMed Abstract:
Mutations in T cell epitopes are implicated in hepatitis C virus (HCV) persistence and can impinge on vaccine development. We recently demonstrated a narrow bias in the human TCR repertoire targeted at an immunodominant, but highly mutable, HLA-B*0801-restricted epitope ((1395)HSKKKCDEL(1403) [HSK]). To investigate if the narrow TCR repertoire facilitates CTL escape, structural and biophysical studies were undertaken, alongside comprehensive functional analysis of T cells targeted at the natural variants of HLA-B*0801-HSK in different HCV genotypes and quasispecies. Interestingly, within the TCR-HLA-B*0801-HSK complex, the TCR contacts all available surface-exposed residues of the HSK determinant. This broad epitope coverage facilitates cross-genotypic reactivity and recognition of common mutations reported in HCV quasispecies, albeit to a varying degree. Certain mutations did abrogate T cell reactivity; however, natural variants comprising these mutations are reportedly rare and transient in nature, presumably due to fitness costs. Overall, despite a narrow bias, the TCR accommodated frequent mutations by acting like a blanket over the hypervariable epitope, thereby providing effective viral immunity. Our findings simultaneously advance the understanding of anti-HCV immunity and indicate the potential for cross-genotype HCV vaccines.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity, University of Melbourne, Parkville, Victoria 3000, Australia;