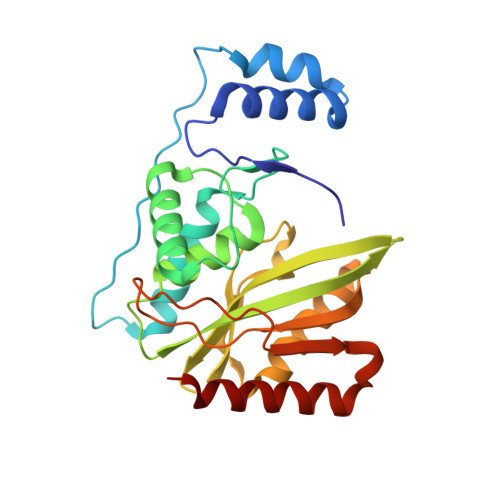
Molecular basis of vasohibins-mediated detyrosination and its impact on spindle function and mitosis.
Liao, S., Rajendraprasad, G., Wang, N., Eibes, S., Gao, J., Yu, H., Wu, G., Tu, X., Huang, H., Barisic, M., Xu, C.(2019) Cell Res 29: 533-547
- PubMed: 31171830
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-019-0187-y
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6J7B, 6J8F, 6J8N, 6J91, 6J9H - PubMed Abstract:
α-Tubulin detyrosination, largely catalyzed by vasohibins, is involved in many microtubule (MT)-related cellular events. In this study, we identified a core heterodimeric complex of human small vasohibin-binding protein (SVBP) and vasohibin 1 (VASH1) (hereafter denoted as SVBP-VASH1) that catalyzes the detyrosination of a peptide derived from C-terminus of α-tubulin. We further solved the crystal structures of the SVBP-VASH1 heterodimer alone and in complex with either an inhibitor or a mutant substrate peptide. Our structural research, complemented by biochemical and mutagenesis experiments, resulted in identification of the key residues for VASH1 binding to SVBP and α-tubulin substrate. Our in vivo experiments reveal that MT detyrosination in general, as well as the interactions between SVBP, VASH1, and α-tubulin, are critical for spindle function and accurate chromosome segregation during mitosis. Furthermore, we found that the phenotypes caused by the depletion of vasohibins were largely rescued upon co-depletion of kinesin13/MCAK, suggesting the coordination between the MT depolymerase and MT detyrosination during mitosis. Thus our work not only provides structural insights into the molecular mechanism of α-tubulin detyrosination catalyzed by SVBP-bound vasohibins, but also uncovers the key role of vasohibins-mediated MT detyrosination in spindle morphology and chromosome segregation during mitosis.
- Hefei National Laboratory for Physical Sciences at Microscale and School of Life Sciences, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China.
Organizational Affiliation: