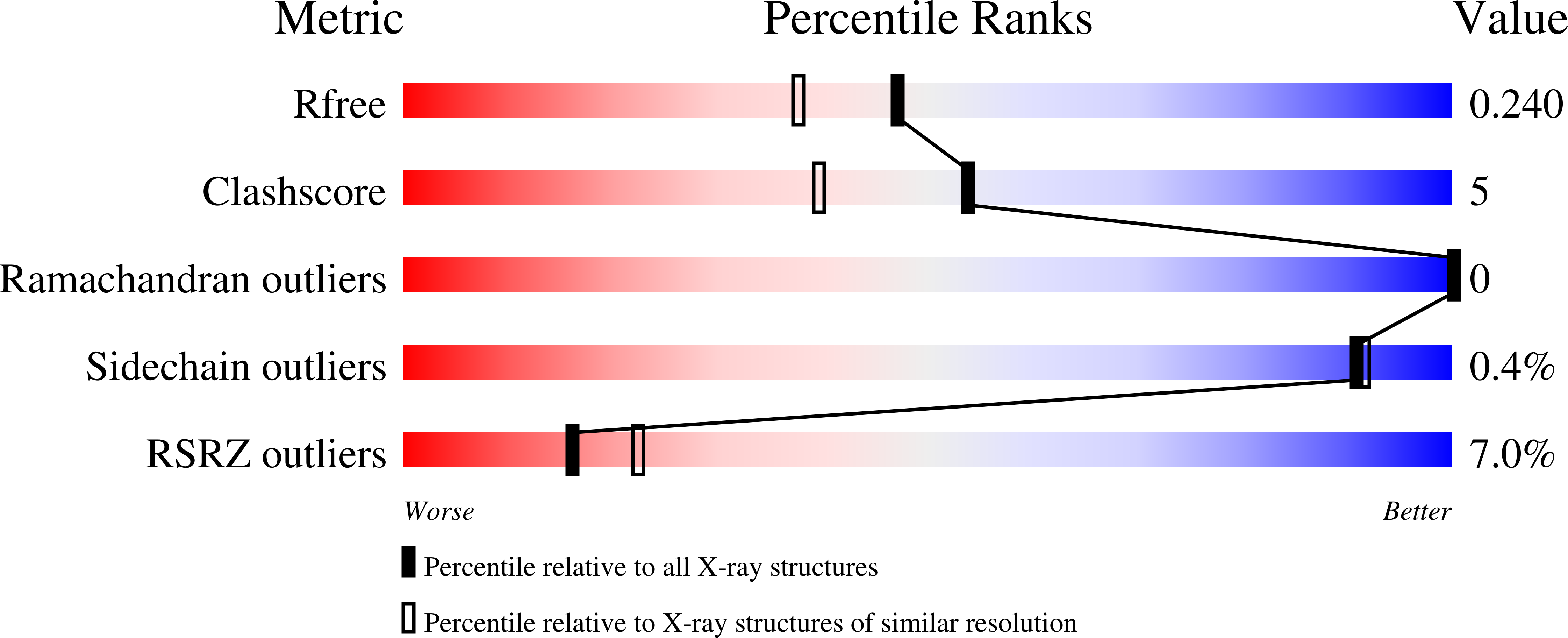
Endogenous vitamin E metabolites mediate allosteric PPAR gamma activation with unprecedented co-regulatory interactions.
Willems, S., Gellrich, L., Chaikuad, A., Kluge, S., Werz, O., Heering, J., Knapp, S., Lorkowski, S., Schubert-Zsilavecz, M., Merk, D.(2021) Cell Chem Biol 28: 1489-1500.e8
- PubMed: 33989565
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2021.04.019
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7AWC, 7AWD - PubMed Abstract:
Vitamin E exhibits pharmacological effects beyond established antioxidant activity suggesting involvement of unidentified mechanisms. Here, we characterize endogenously formed tocopherol carboxylates and the vitamin E mimetic garcinoic acid (GA) as activators of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ). Co-stimulation of PPARγ with GA and the orthosteric agonist pioglitazone resulted in additive transcriptional activity. In line with this, the PPARγ-GA complex adopted a fully active conformation and interestingly contained two bound GA molecules with one at an allosteric site. A co-regulator interaction scan demonstrated an unanticipated co-factor recruitment profile for GA-bound PPARγ compared with canonical PPARγ agonists and gene expression analysis revealed different effects of GA and pioglitazone on PPAR signaling in hepatocytes. These observations reveal allosteric mechanisms of PPARγ modulation as an alternative avenue to PPARγ targeting and suggest contributions of PPARγ activation by α-13-tocopherolcarboxylate to the pharmacological effects of vitamin E.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Goethe University Frankfurt, Frankfurt 60438, Germany.