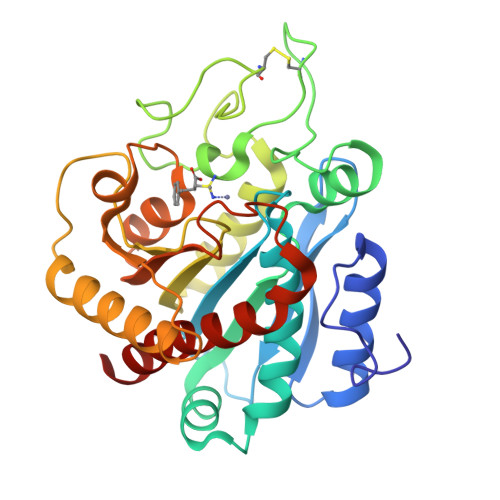
Structural comparison of sulfodiimine and sulfonamide inhibitors in their complexes with zinc enzymes.
Cappalonga, A.M., Alexander, R.S., Christianson, D.W.(1992) J Biological Chem 267: 19192-19197
- PubMed: 1527041
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.2210/pdb1cps/pdb
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1CPS - PubMed Abstract:
The three-dimensional structure of (L(-)-2-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl) methylsulfodiimine in its complex with the zinc metalloenzyme carboxypeptidase A has been determined at 2.25-A resolution by x-ray crystallographic methods. This is the first example of a sulfodiimine-containing inhibitor binding to a zinc enzyme, and the structure of the enzyme-inhibitor complex reveals that the tetrahedral sulfodiimine group coordinates to the active site zinc ion in unidentate fashion. The zinc-coordinated nitrogen atom of the sulfodiimine group is also within hydrogen bonding distance to active site base Glu-270; presumably, the sulfodiimine is ionized and accepts a hydrogen bond from protonated Glu-270. The other sulfodiimine nitrogen accepts a hydrogen bond from Arg-127, and the inhibitor binds as a possible analogue of the tetrahedral transition state (or intermediate) in a promoted water pathway for peptide hydrolysis. The unidentate sulfodiimine-zinc binding mode observed in this enzyme-inhibitor complex is reminiscent of that observed in sulfonamide complexes with the zinc metalloenzyme carbonic anhydrase II, and the structural features of sulfodiimine- and sulfonamide-zinc interactions exhibit important similarities among recently determined structures of enzyme-inhibitor complexes: ionized nitrogens bind to zinc in each structure, and these nitrogens are engaged in hydrogen bond interactions with neighboring enzyme residues.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia 19104-6323.