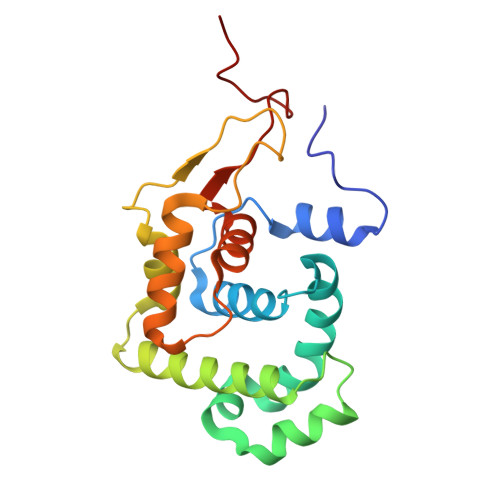
3-Methyladenine DNA glycosylase I is an unexpected helix-hairpin-helix superfamily member.
Drohat, A.C., Kwon, K., Krosky, D.J., Stivers, J.T.(2002) Nat Struct Biol 9: 659-664
- PubMed: 12161745
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb829
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1LMZ - PubMed Abstract:
The Escherichia coli enzyme 3-methyladenine DNA glycosylase I (TAG) hydrolyzes the glycosidic bond of 3-methyladenine (3-MeA) in DNA and is found in many bacteria and some higher eukaryotes. TAG shows little primary sequence identity with members of the well-known helix-hairpin-helix (HhH) superfamily of DNA repair glycosylases, which consists of AlkA, EndoIII, MutY and hOGG1. Unexpectedly, the three-dimensional solution structure reported here reveals TAG as member of this superfamily. The restricted specificity of TAG for 3-MeA bases probably arises from its unique aromatic rich 3-MeA binding pocket and the absence of a catalytic aspartate that is present in all other HhH family members.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Pharmacology and Molecular Sciences, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, 725 North Wolfe Street, Baltimore, Maryland 21205-2185, USA.