X-ray structure of a water-soluble analog of the membrane protein phospholamban: sequence determinants defining the topology of tetrameric and pentameric coiled coils.
Slovic, A.M., Stayrook, S.E., North, B., DeGrado, W.F.(2005) J Mol Biology 348: 777-787
- PubMed: 15826670
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2005.02.040
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1YOD - PubMed Abstract:
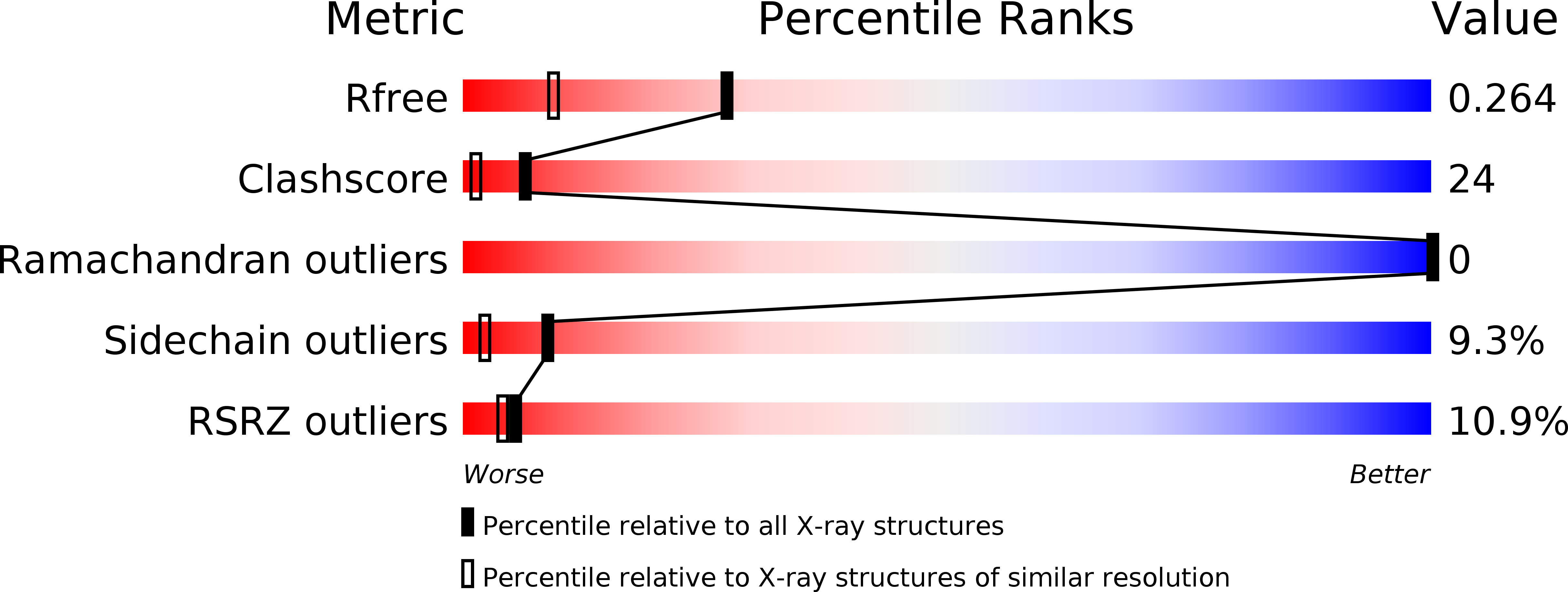
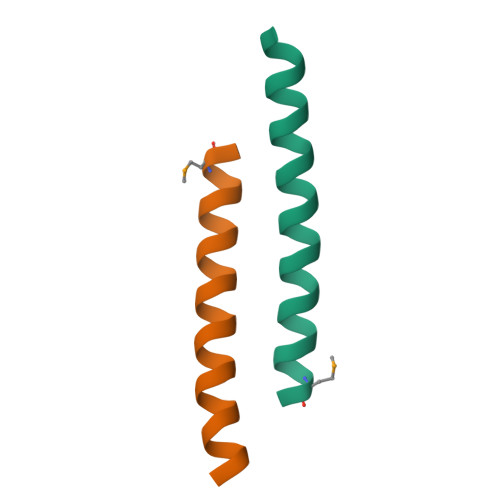
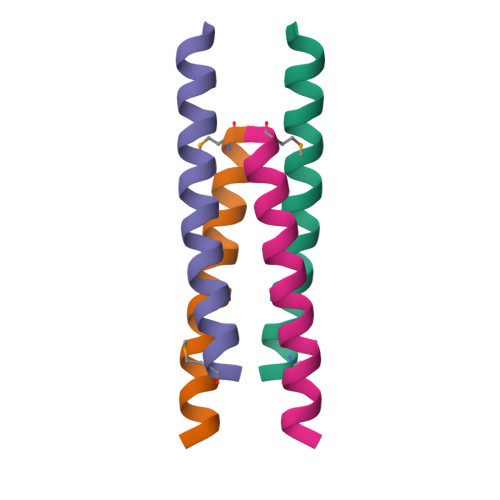
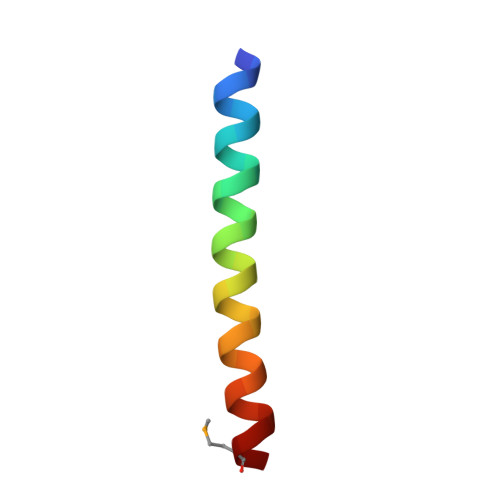
Phospholamban (PLB) is a pentameric transmembrane protein that regulates the Ca(2+)-dependent ATPase SERCA2a in sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. We previously described the computational design of a water-soluble variant of phospholamban, WSPLB, which reproduced many of the structural and functional properties of the native membrane-soluble protein. While the full-length WSPLB forms a pentamer in solution, a truncated variant forms very stable tetramers. To obtain insight into the tetramer-pentamer cytoplasmic switch, we solved the crystal structure of the truncated construct, WSPLB 21-52. This peptide has a heptad sequence repeat with Leu residues at a- and Ile at d-positions from residues 31-52. The crystal structure revealed that WSPLB 21-52 adopted an antiparallel tetrameric coiled coil. This topology contrasts with the parallel topology of an analogue of the coiled-coil of GCN4 with the same Leu(a) Ile(d) repeat. Analysis of these structures revealed how the nature of the partially exposed residues at e- and g-positions influence the topology formed by the bundle. We also constructed a model for the pentameric form of PLB using the coiled-coil parameters derived from a single monomer in the tetrameric structure. This model suggests that both buried and interfacial hydrogen bonds are important for stabilizing the parallel pentamer.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics, School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA.