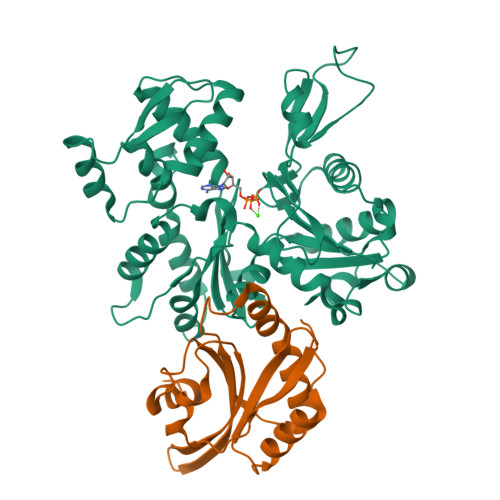
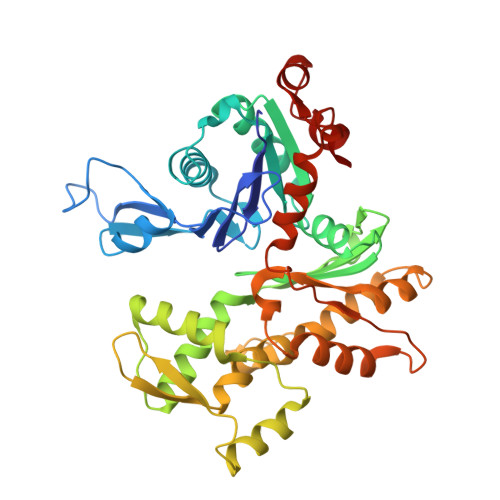
Structure of the actin-depolymerizing factor homology domain in complex with actin
Paavilainen, V.O., Oksanen, E., Goldman, A., Lappalainen, P.(2008) J Cell Biol 182: 51-59
- PubMed: 18625842
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200803100
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3DAW - PubMed Abstract:
Actin dynamics provide the driving force for many cellular processes including motility and endocytosis. Among the central cytoskeletal regulators are actin-depolymerizing factor (ADF)/cofilin, which depolymerizes actin filaments, and twinfilin, which sequesters actin monomers and caps filament barbed ends. Both interact with actin through an ADF homology (ADF-H) domain, which is also found in several other actin-binding proteins. However, in the absence of an atomic structure for the ADF-H domain in complex with actin, the mechanism by which these proteins interact with actin has remained unknown. Here, we present the crystal structure of twinfilin's C-terminal ADF-H domain in complex with an actin monomer. This domain binds between actin subdomains 1 and 3 through an interface that is conserved among ADF-H domain proteins. Based on this structure, we suggest a mechanism by which ADF/cofilin and twinfilin inhibit nucleotide exchange of actin monomers and present a model for how ADF/cofilin induces filament depolymerization by weakening intrafilament interactions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Program in Cellular Biotechnology, Institute of Biotechnology, University of Helsinki, Helsinki FIN-00014, Finland.