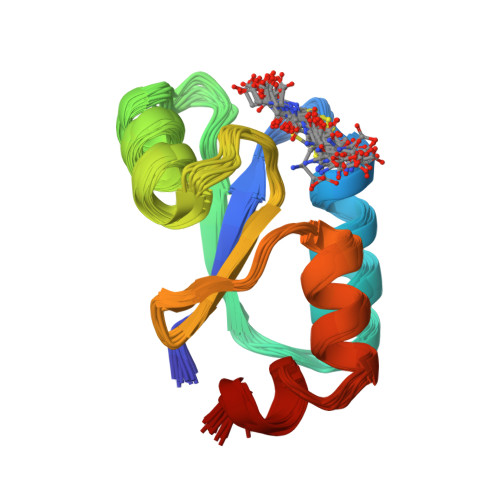
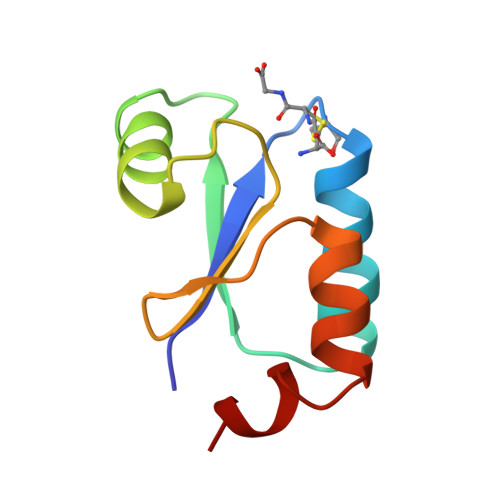
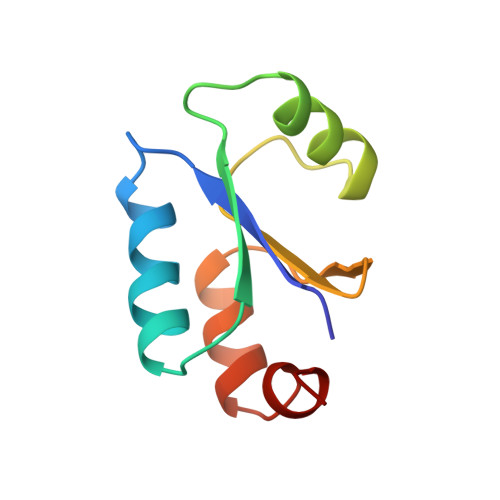
NMR structure of Escherichia coli glutaredoxin 3-glutathione mixed disulfide complex: implications for the enzymatic mechanism.
Nordstrand, K., slund, F., Holmgren, A., Otting, G., Berndt, K.D.(1999) J Mol Biology 286: 541-552
- PubMed: 9973569
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1998.2444
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
3GRX - PubMed Abstract:
Glutaredoxins (Grxs) catalyze reversible oxidation/reduction of protein disulfide groups and glutathione-containing mixed disulfide groups via an active site Grx-glutathione mixed disulfide (Grx-SG) intermediate. The NMR solution structure of the Escherichia coli Grx3 mixed disulfide with glutathione (Grx3-SG) was determined using a C14S mutant which traps this intermediate in the redox reaction. The structure contains a thioredoxin fold, with a well-defined binding site for glutathione which involves two intermolecular backbone-backbone hydrogen bonds forming an antiparallel intermolecular beta-bridge between the protein and glutathione. The solution structure of E. coli Grx3-SG also suggests a binding site for a second glutathione in the reduction of the Grx3-SG intermediate, which is consistent with the specificity of reduction observed in Grxs. Molecular details of the structure in relation to the stability of the intermediate and the activity of Grx3 as a reductant of glutathione mixed disulfide groups are discussed. A comparison of glutathione binding in Grx3-SG and ligand binding in other members of the thioredoxin superfamily is presented, which illustrates the highly conserved intermolecular interactions in this protein family.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics, Karolinska Institute, S-171 77, Stockholm, Sweden.