The Molybdenum Storage Protein: A soluble ATP hydrolysis-dependent molybdate pump.
Poppe, J., Brunle, S., Hail, R., Wiesemann, K., Schneider, K., Ermler, U.(2018) FEBS J 285: 4602-4616
- PubMed: 30367742
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.14684
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6GU5, 6GUJ, 6GWV, 6GX4 - PubMed Abstract:
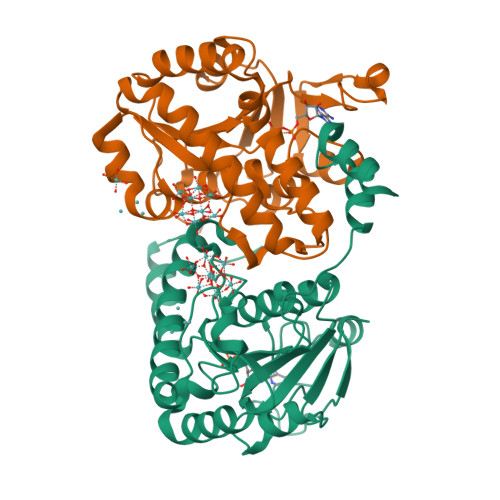
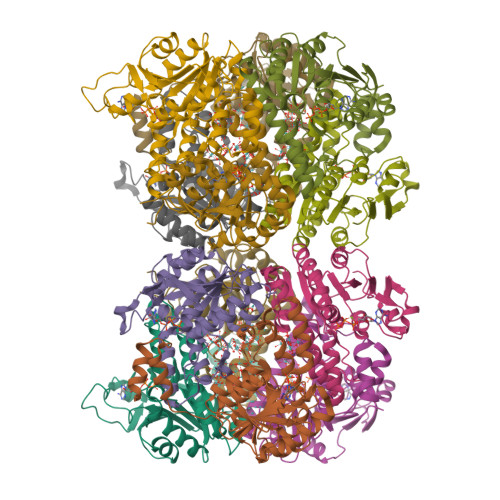
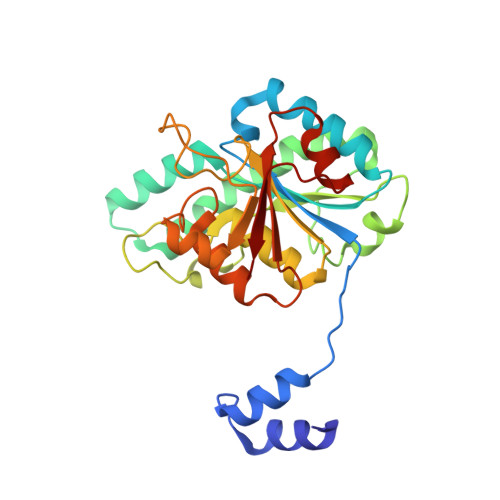
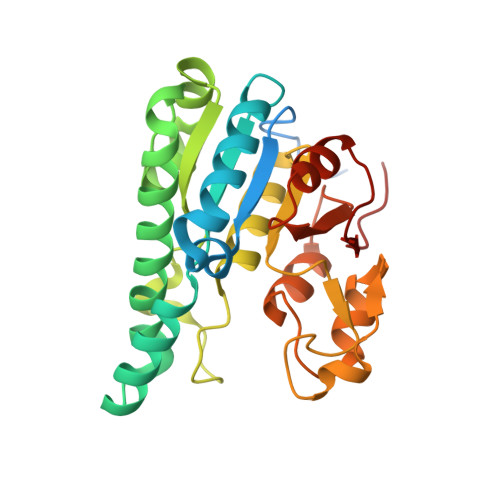
A continuous FeMo cofactor supply for nitrogenase maturation is ensured in Azotobacter vinelandii by developing a cage-like molybdenum storage protein (MoSto) capable to store ca. 120 molybdate molecules (
4 2 - ) as discrete polyoxometalate (POM) clusters. To gain mechanistic insight into this process, MoSto was characterized by Mo and ATP/ADP content, structural, and kinetic analysis. We defined three functionally relevant states specified by the presence of both ATP/ADP and POM clusters (MoSto funct ), of only ATP/ADP (MoSto basal ) and of neither ATP/ADP nor POM clusters (MoSto zero ), respectively. POM clusters are only produced when ATP is hydrolyzed to ADP and phosphate. V max was ca. 13 μmol phosphate ·min -1 ·mg -1 and K m for molybdate and ATP/Mg 2+ in the low micromolar range. ATP hydrolysis presumably proceeds at subunit α, inferred from a highly occupied α-ATP/Mg 2+ and a weaker occupied β-ATP/no Mg 2+ -binding site found in the MoSto funct structure. Several findings indicate that POM cluster storage is separated into a rapid ATP hydrolysis-dependent molybdate transport across the protein cage wall and a slow molybdate assembly induced by combined auto-catalytic and protein-driven processes. The cage interior, the location of the POM cluster depot, is locked in all three states and thus not rapidly accessible for molybdate from the outside. Based on V max , the entire Mo storage process should be completed in less than 10 s but requires, according to the molybdate content analysis, ca. 15 min. Long-time incubation of MoSto basal with nonphysiological high molybdate amounts implicates an equilibrium in and outside the cage and POM cluster self-formation without ATP hydrolysis. DATABASES: The crystal structures MoSto in the MoSto-F6, MoSto-F7, MoSto basal , MoSto zero , and MoSto-F1 vitro states were deposited to PDB under the accession numbers PDB 6GU5, 6GUJ, 6GWB, 6GWV, and 6GX4.
Organizational Affiliation:
Max-Planck-Institut für Biophysik, Frankfurt am Main, Germany.