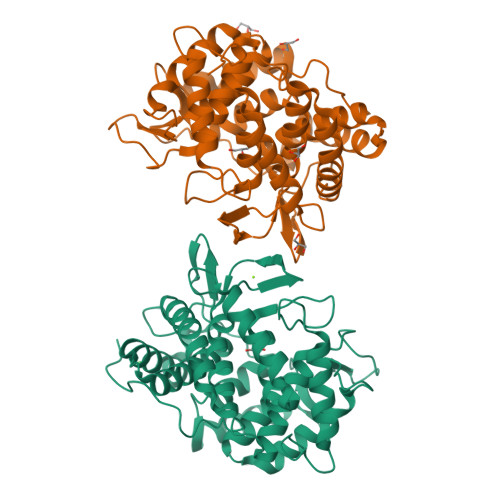
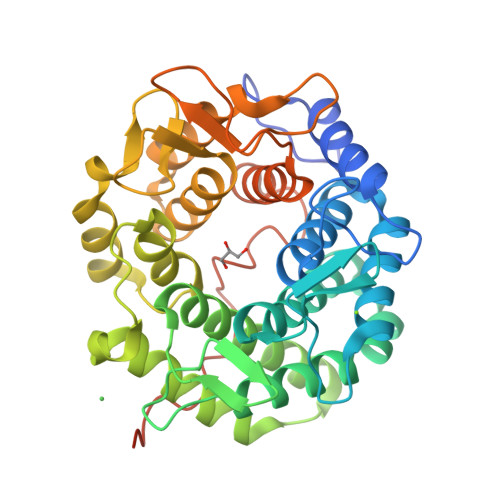
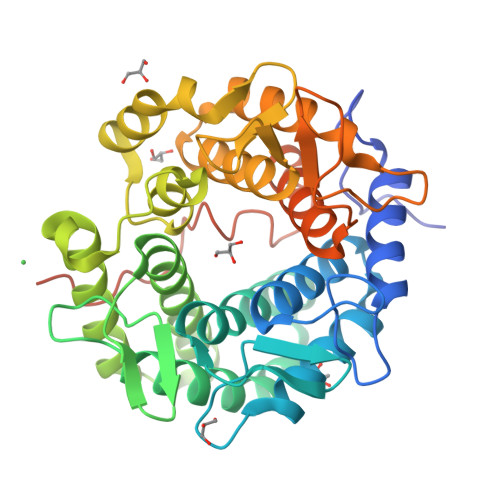
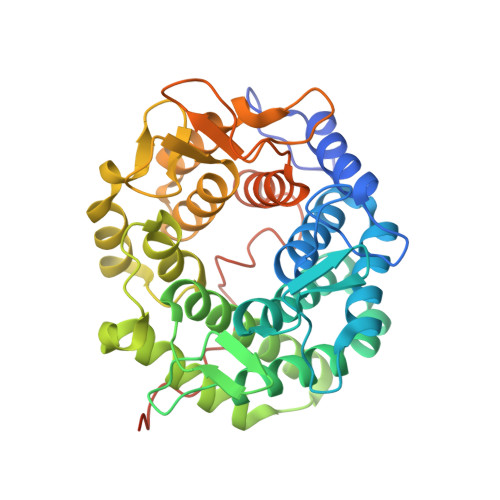
Self-recycling and partially conservative replication of mycobacterial methylmannose polysaccharides.
Maranha, A., Costa, M., Ripoll-Rozada, J., Manso, J.A., Miranda, V., Mendes, V.M., Manadas, B., Macedo-Ribeiro, S., Ventura, M.R., Pereira, P.J.B., Empadinhas, N.(2023) Commun Biol 6: 108-108
- PubMed: 36707645
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-023-04448-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7QSG, 7QSJ - PubMed Abstract:
The steep increase in nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) infections makes understanding their unique physiology an urgent health priority. NTM synthesize two polysaccharides proposed to modulate fatty acid metabolism: the ubiquitous 6-O-methylglucose lipopolysaccharide, and the 3-O-methylmannose polysaccharide (MMP) so far detected in rapidly growing mycobacteria. The recent identification of a unique MMP methyltransferase implicated the adjacent genes in MMP biosynthesis. We report a wide distribution of this gene cluster in NTM, including slowly growing mycobacteria such as Mycobacterium avium, which we reveal to produce MMP. Using a combination of MMP purification and chemoenzymatic syntheses of intermediates, we identified the biosynthetic mechanism of MMP, relying on two enzymes that we characterized biochemically and structurally: a previously undescribed α-endomannosidase that hydrolyses MMP into defined-sized mannoligosaccharides that prime the elongation of new daughter MMP chains by a rare α-(1→4)-mannosyltransferase. Therefore, MMP biogenesis occurs through a partially conservative replication mechanism, whose disruption affected mycobacterial growth rate at low temperature.
Organizational Affiliation:
CNC - Center for Neuroscience and Cell Biology, University of Coimbra, 3004-504, Coimbra, Portugal.