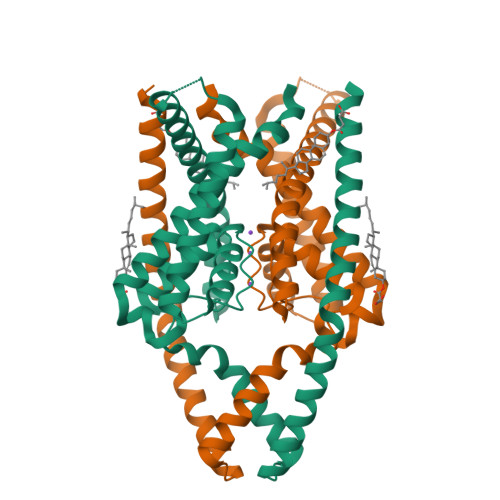
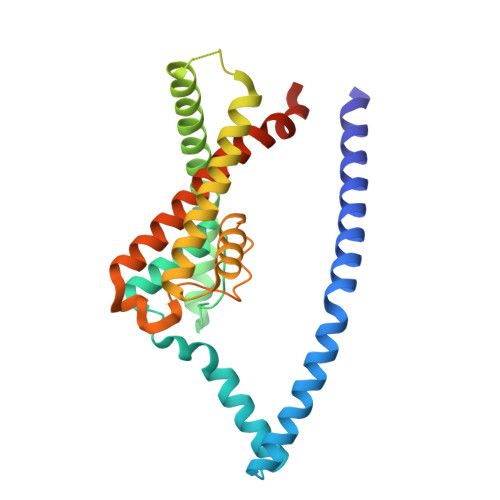
Structures of TASK-1 and TASK-3 K2P channels provide insight into their gating and dysfunction in disease.
Hall, P.R., Jouen-Tachoire, T., Schewe, M., Proks, P., Baukrowitz, T., Carpenter, E.P., Newstead, S., Rodstrom, K.E.J., Tucker, S.J.(2025) Structure 33: 115
- PubMed: 39637865
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2024.11.005
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9G9V, 9G9W, 9G9X - PubMed Abstract:
TASK-1 and TASK-3 are pH-sensitive two-pore domain (K2P/KCNK) K + channels. Their functional roles make them promising targets for treatment of multiple disorders including sleep apnea, pain, and atrial fibrillation. Mutations in these channels are also associated with neurodevelopmental and hypertensive disorders. A previous crystal structure of TASK-1 revealed a lower "X-gate" as a hotspot for missense gain-of-function (GoF) mutations associated with DDSA (developmental delay with sleep apnea). However, the mechanisms of gating in TASK channels are still not fully understood. Here, we resolve structures for both human TASK-1 and TASK-3 by cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM), as well as a recurrent TASK-3 variant (G236R) associated with KCNK9 imprinting syndrome (KIS) (formerly known as Birk-Barel syndrome). Combined with functional studies of the X-gating mechanism, we provide evidence for how a highly conserved gating mechanism becomes defective in disease, and also provide further insight into the pathway of conformational changes that underlie the pH-dependent inhibition of TASK channel activity.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK; Clarendon Laboratory, Department of Physics, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK; Scripps Institute, San Diego, CA, USA; Kavli Institute for Nanoscience Discovery, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK.