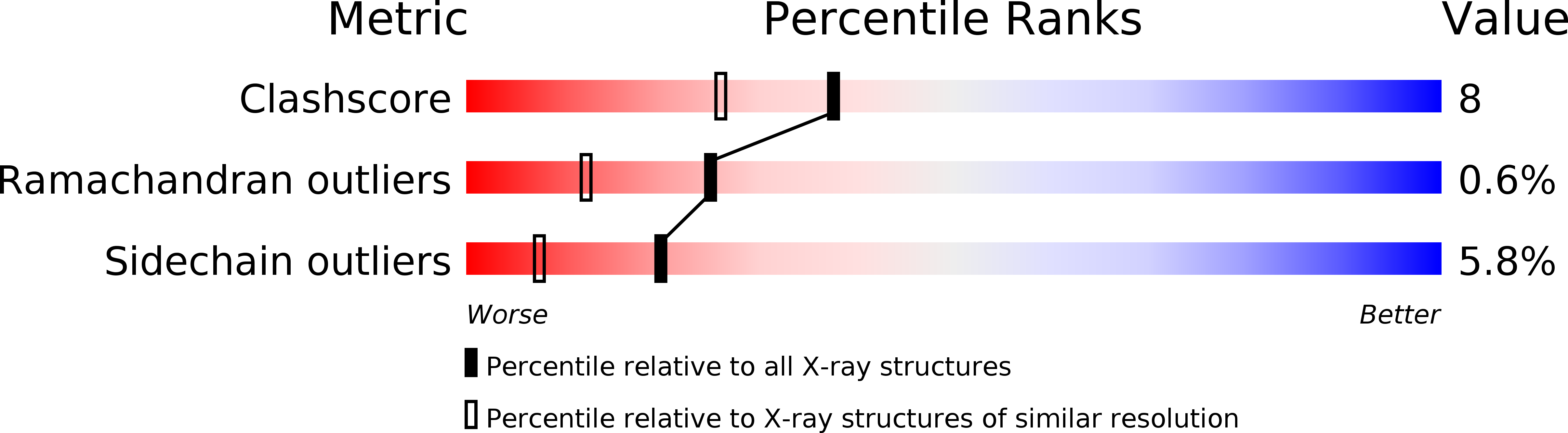
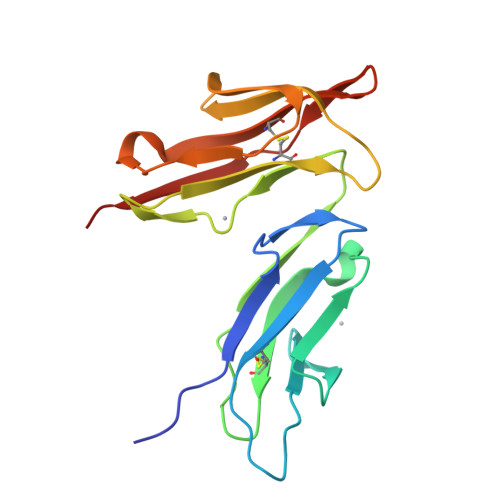
Crystal structure of the extracellular domain of a human Fc gamma RIII.
Zhang, Y., Boesen, C.C., Radaev, S., Brooks, A.G., Fridman, W.H., Sautes-Fridman, C., Sun, P.D.(2000) Immunity 13: 387-395
- PubMed: 11021536
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1074-7613(00)00038-8
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1FNL - PubMed Abstract:
Fc receptors play a major role in immune defenses against pathogens and in inflammatory processes. The crystal structure of a human immunoglobulin receptor, FcgammaRIIIb, has been determined to 1.8 A resolution. The overall fold consists of two immunoglobulin-like domains with an acute interdomain hinge angle of approximately 50 degrees. Trp-113, wedged between the N-terminal D1 and the C-terminal D2 domains, appears to further restrict the hinge angle. The putative Fc binding region of the receptor carries a net positive charge complementary to the negative-charged receptor binding regions on Fc. A 1:1 binding stoichiometry between the receptor and Fc was measured by both the equilibrium and nonequilibrium size-exclusion chromatography. Two separate parallel dimers are observed in the crystal lattice, offering intriguing models for receptor aggregation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Human Biological Chemistry and Genetics, University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston 77555, USA.