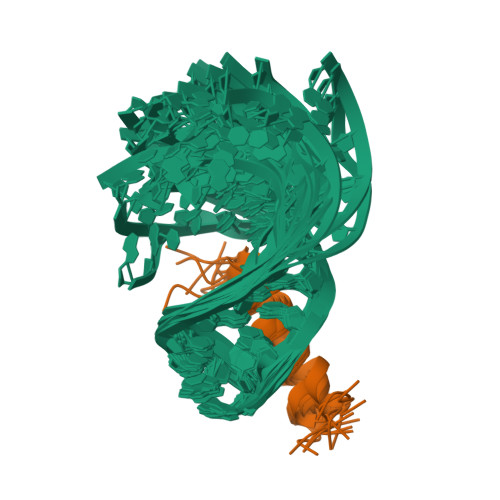
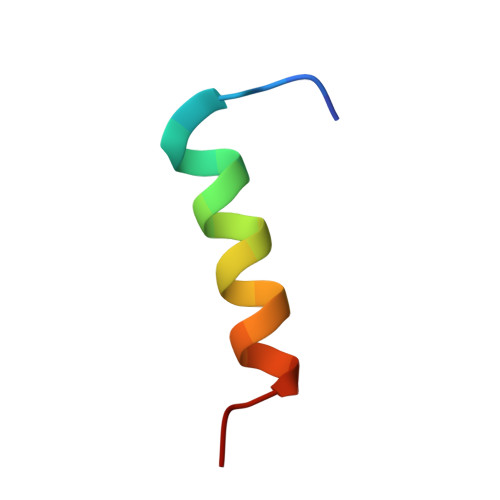
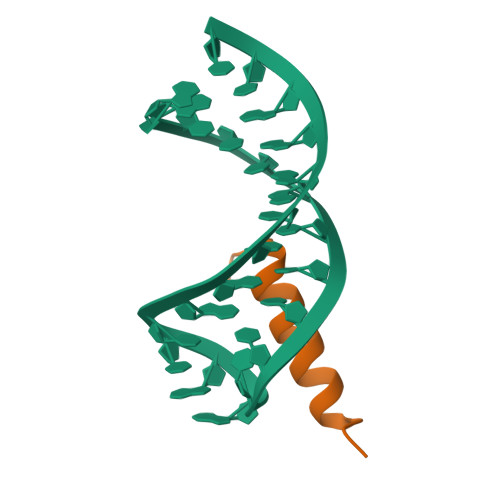
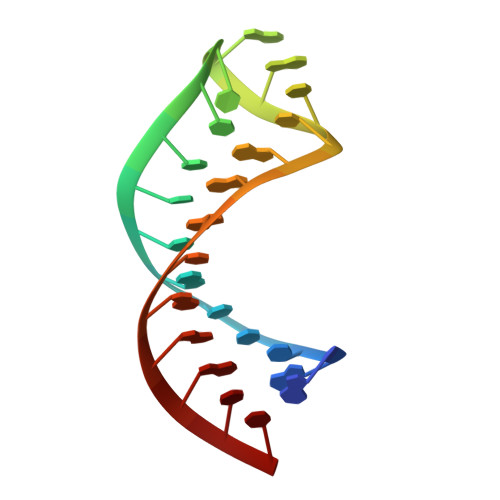
Structural mimicry in the phage phi21 N peptide-boxB RNA complex
Cilley, C.D., Williamson, J.R.(2003) RNA 9: 663-676
- PubMed: 12756325
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.2189203
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1NYB - PubMed Abstract:
We determined the solution structure of a 22-amino-acid peptide from the amino-terminal domain of the bacteriophage phi21 N protein in complex with its cognate 24-mer boxB RNA hairpin using heteronuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The N peptide binds as an alpha-helix and interacts predominately with the major groove side of the 5' half of the boxB RNA stem-loop. This binding interface is defined by surface complementarity of polar and nonpolar interactions, and little sequence-specific recognition. The phi21 boxB loop (CUAACC) has hydrogen bond and backbone torsions typical of the "U-turn" motif, as well as base stacking of the last 4 nt, and a hydrogen bonded C:C pair closing the loop. The exposed face of the phi21 boxB loop, in complex with the N peptide, is strikingly similar to the GNRA tetraloop-like folds of the related lambda and P22 bacteriophage N peptide-boxB RNA complexes. The N peptide-boxB complexes of the various phage, while individually distinct, provide similar structural features for interactions with the Escherichia coli host factors to enable antitermination.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biology, The Scripps Research Institute, La Jolla, California 92037, USA.