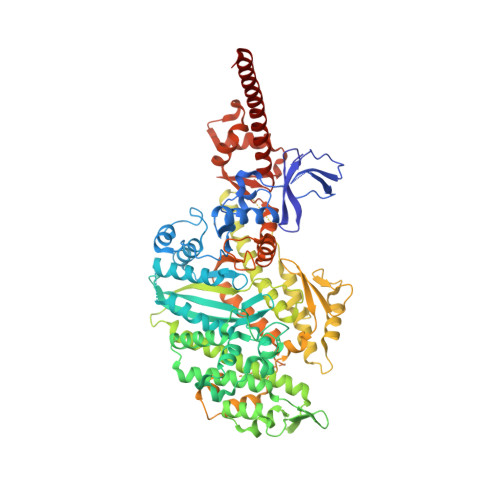
A Structural State of the Myosin V Motor without Bound Nucleotide
Coureux, P.-D., Wells, A.L., Menetrey, J., Yengo, C.M., Morris, C.A., Sweeney, H.L., Houdusse, A.(2003) Nature 425: 419
- PubMed: 14508494
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01927
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1OE9 - PubMed Abstract:
The myosin superfamily of molecular motors use ATP hydrolysis and actin-activated product release to produce directed movement and force. Although this is generally thought to involve movement of a mechanical lever arm attached to a motor core, the structural details of the rearrangement in myosin that drive the lever arm motion on actin attachment are unknown. Motivated by kinetic evidence that the processive unconventional myosin, myosin V, populates a unique state in the absence of nucleotide and actin, we obtained a 2.0 A structure of a myosin V fragment. Here we reveal a conformation of myosin without bound nucleotide. The nucleotide-binding site has adopted new conformations of the nucleotide-binding elements that reduce the affinity for the nucleotide. The major cleft in the molecule has closed, and the lever arm has assumed a position consistent with that in an actomyosin rigor complex. These changes have been accomplished by relative movements of the subdomains of the molecule, and reveal elements of the structural communication between the actin-binding interface and nucleotide-binding site of myosin that underlie the mechanism of chemo-mechanical transduction.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Motility, Institut Curie CNRS, UMR144, 26 rue d'Ulm, 75248 Paris cedex 05, France.