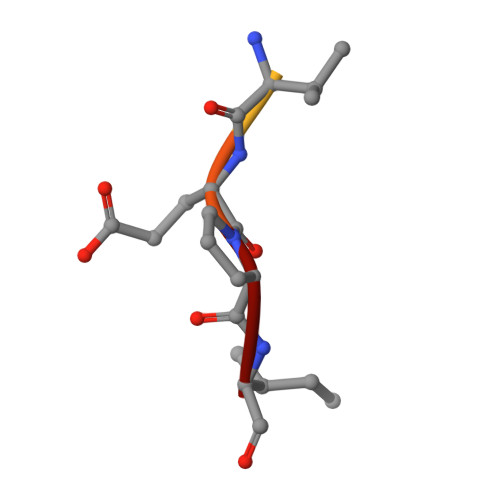
Structure of a Specific Acyl-Enzyme Complex Formed between Beta-Casomorphin-7 and Porcine Pancreatic Elastase
Wilmouth, R.C., Clifton, I.J., Robinson, C.V., Roach, P.L., Aplin, R.T., Westwood, N.J., Hajdu, J., Schofield, C.J.(1997) Nat Struct Biol 4: 456
- PubMed: 9187653
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0697-456
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1QIX - PubMed Abstract:
Mass spectrometric screening reveals that an unmodified natural heptapeptide--human beta-casomorphin-7, an internal sequence of human beta-casein that possesses opioid-like activity--reacts with porcine pancreatic elastase to form an unusually stable acyl-enzyme complex at low pH. X-ray crystallographic analysis (to 1.9 A resolution) at pH 5 shows continuous electron density linking the C-terminal isoleucine of beta-casomorphin-7 to Ser 195 through an ester bond. The structure reveals a well defined water molecule (Wat 317), equidistant between the carbon of the ester carbonyl and N epsilon 2 of His 57. Deprotonation of Wat 317 will produce a hydroxide ion positioned to attack the ester carbonyl through the favoured Bürgi-Dunitz trajectory.
- Oxford Centre for Molecular Sciences, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: