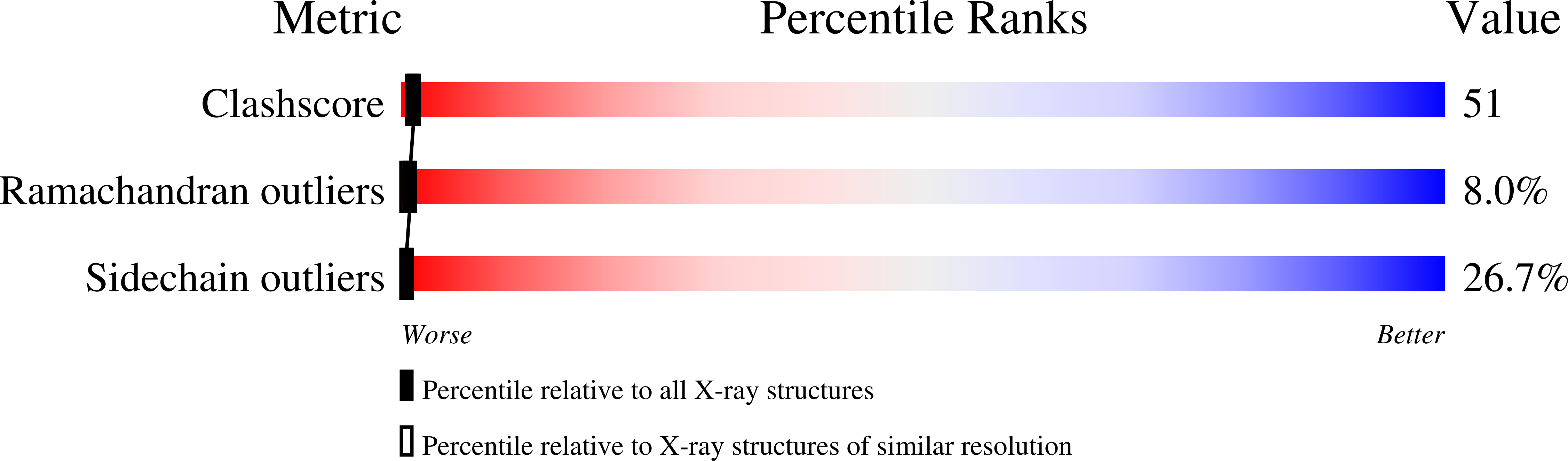Application of crystallographic and modeling methods in the design of purine nucleoside phosphorylase inhibitors.
Ealick, S.E., Babu, Y.S., Bugg, C.E., Erion, M.D., Guida, W.C., Montgomery, J.A., Secrist 3rd., J.A.(1991) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88: 11540-11544
- PubMed: 1763067
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.88.24.11540
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1ULA, 1ULB - PubMed Abstract:
Competitive inhibitors of the salvage pathway enzyme purine-nucleoside phosphorylase (purine-nucleoside:orthophosphate ribosyltransferase, EC 2.4.2.1) have been designed by using the three-dimensional structure of the enzyme as determined by x-ray crystallography. The process was an iterative one that utilized interactive computer graphics, Monte Carlo-based conformational searching, energy minimization, and x-ray crystallography. The proposed compounds were synthesized and tested by an in vitro assay. Among the compounds designed and synthesized are the most potent competitive inhibitors of purine nucleoside phosphorylase thus far reported.
Organizational Affiliation:
University of Alabama, Birmingham 35294.