Structural basis of HutP-mediated anti-termination and roles of the Mg2+ ion and L-histidine ligand.
Kumarevel, T., Mizuno, H., Kumar, P.K.(2005) Nature 434: 183-191
- PubMed: 15758992
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03355
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1WMQ, 1WPS, 1WPV - PubMed Abstract:
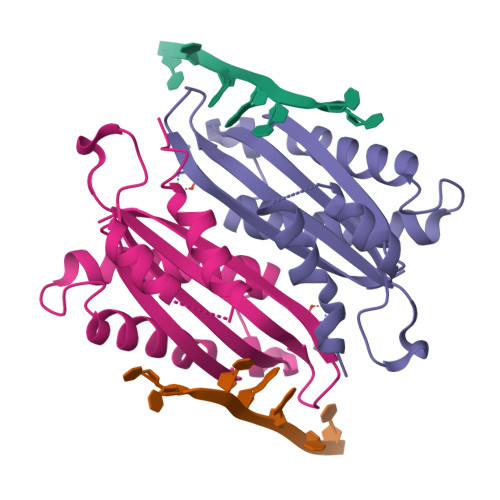
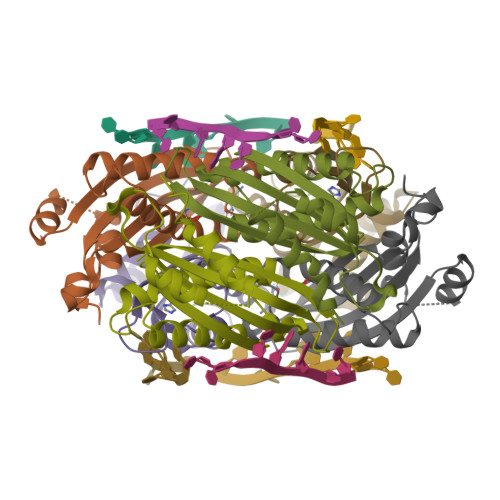
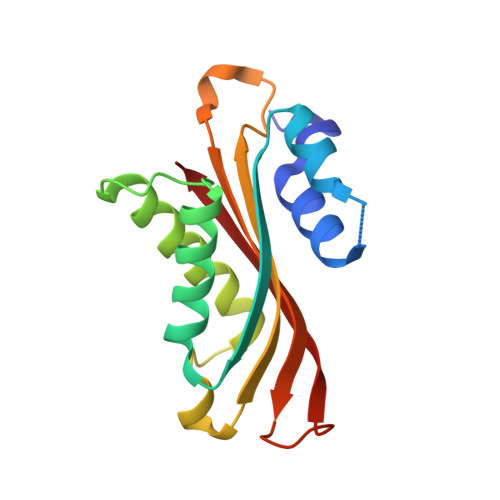
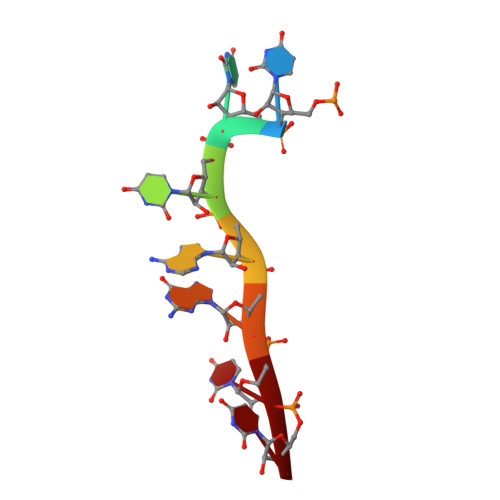
HutP regulates the expression of the hut structural genes of Bacillus subtilis by an anti-termination mechanism and requires two components, Mg2+ ions and L-histidine. HutP recognizes three UAG triplet units, separated by four non-conserved nucleotides on the terminator region. Here we report the 1.60-A resolution crystal structure of the quaternary complex (HutP-L-histidine-Mg2+-21-base single-stranded RNA). In the complex, the RNA adopts a novel triangular fold on the hexameric surface of HutP, without any base-pairing, and binds to the protein mostly by specific protein-base interactions. The structure explains how the HutP and RNA interactions are regulated critically by the l-histidine and Mg2+ ion through the structural rearrangement. To gain insights into these structural rearrangements, we solved two additional crystal structures (uncomplexed HutP and HutP-L-histidine-Mg2+) that revealed the intermediate structures of HutP (before forming an active structure) and the importance of the Mg2+ ion interactions in the complexes.
Organizational Affiliation:
Functional Nucleic Acids Group, Institute for Biological Resources and Functions, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Central 6, 1-1-1 Higashi, Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-8566, Japan.