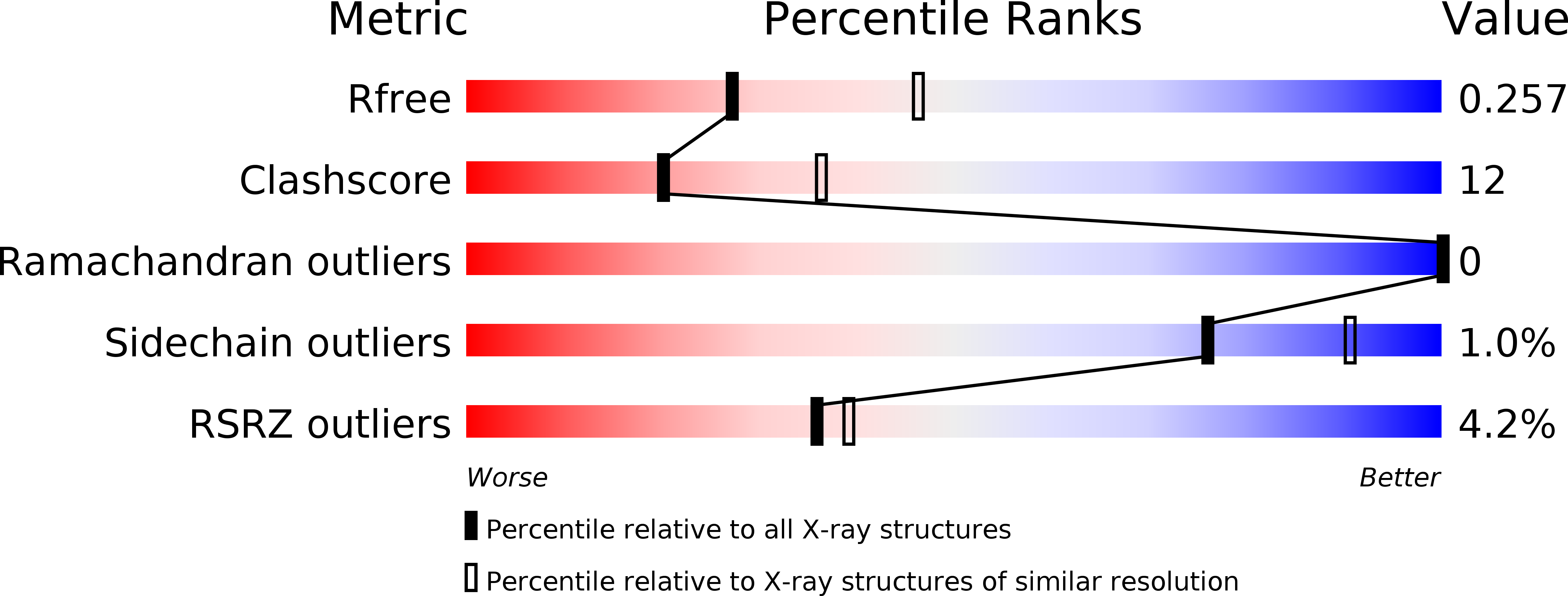
Structural basis for bile salt inhibition of pancreatic phospholipase A2.
Pan, Y.H., Bahnson, B.J.(2007) J Mol Biol 369: 439-450
- PubMed: 17434532
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2007.03.034
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2AZY, 2AZZ, 2B00, 2B01, 2B03, 2B04 - PubMed Abstract:
Bile salt interactions with phospholipid monolayers of fat emulsions are known to regulate the actions of gastrointestinal lipolytic enzymes in order to control the uptake of dietary fat. Specifically, on the lipid/aqueous interface of fat emulsions, the anionic portions of amphipathic bile salts have been thought to interact with and activate the enzyme group-IB phospholipase A2 (PLA2) derived from the pancreas. To explore this regulatory process, we have determined the crystal structures of the complexes of pancreatic PLA2 with the naturally occurring bile salts: cholate, glycocholate, taurocholate, glycochenodeoxycholate, and taurochenodeoxycholate. The five PLA2-bile salt complexes each result in a partly occluded active site, and the resulting ligand binding displays specific hydrogen bonding interactions and extensive hydrophobic packing. The amphipathic bile salts are bound to PLA2 with their polar hydroxyl and sulfate/carboxy groups oriented away from the enzyme's hydrophobic core. The impaired catalytic and interface binding functions implied by these structures provide a basis for the previous numerous observations of a biphasic dependence of the rate of PLA2 catalyzed hydrolysis of zwitterionic glycerophospholipids in the presence of bile salts. The rising or activation phase is consistent with enhanced binding and activation of the bound PLA2 by the bile salt induced anionic charge in a zwitterionic interface. The falling or inhibitory phase can be explained by the formation of a catalytically inert stoichiometric complex between PLA2 and any bile salts in which it forms a stable complex. The model provides new insight into the regulatory role that specific PLA2-bile salt interactions are likely to play in fat metabolism.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Delaware, Newark, Delaware 19716, USA.