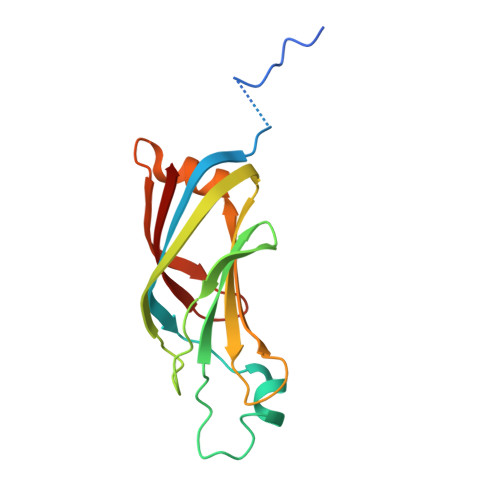
Structure of human protein kinase C eta (PKCeta) C2 domain and identification of phosphorylation sites.
Littler, D.R., Walker, J.R., She, Y.M., Finerty, P.J., Newman, E.M., Dhe-Paganon, S.(2006) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 349: 1182-1189
- PubMed: 16973127
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.08.160
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2FK9 - PubMed Abstract:
Protein kinase C eta (PKCeta) is one of several PKC isoforms found in humans. It is a novel PKC isoform in that it is activated by diacylglycerol and anionic phospholipids but not calcium. The crystal structure of the PKCeta-C2 domain, which is thought to mediate anionic phospholipid sensing in the protein, was determined at 1.75 A resolution. The structure is similar to that of the PKC epsilon C2 domain but with significant variations at the putative lipid-binding site. Two serine residues within PKC eta were identified in vitro as potential autophosphorylation sites. In the unphosphorylated structure both serines line the putative lipid-binding site and may therefore play a role in the lipid-regulation of the kinase.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Genomics Consortium, University of Toronto, 100 College Street, Toronto, Ont., Canada M5G 1L5.