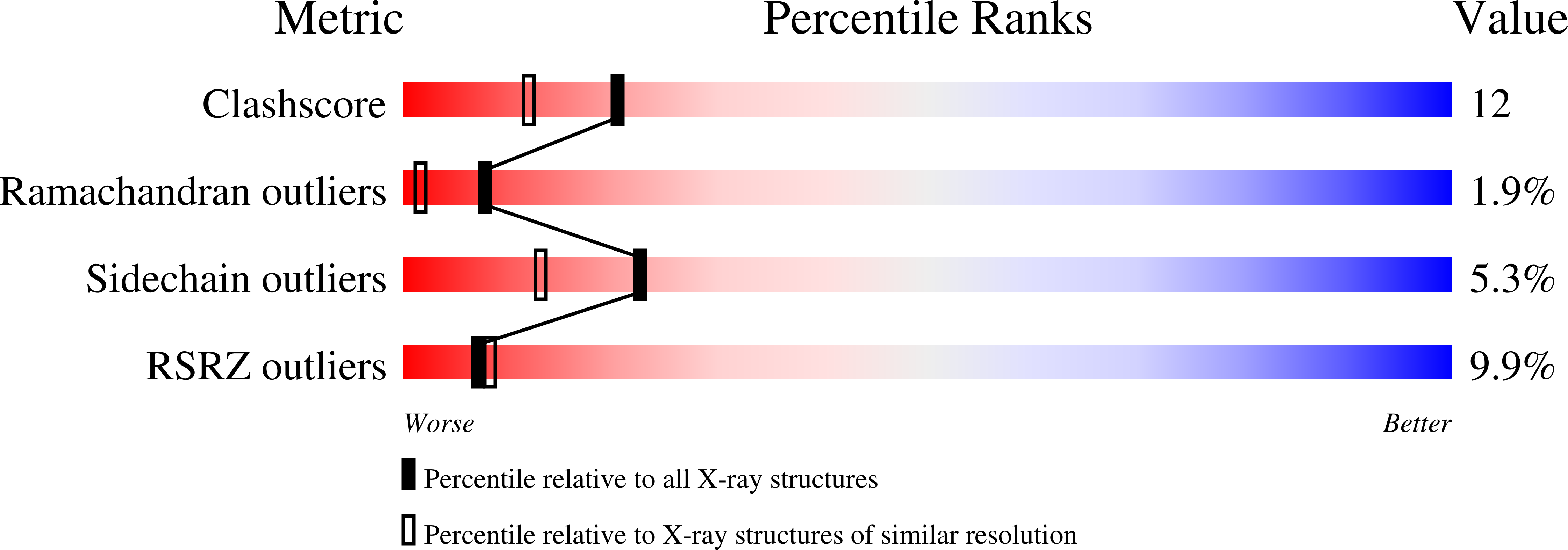The structure of the R184A mutant of the inositol monophosphatase encoded by suhB and implications for its functional interactions in Escherichia coli.
Wang, Y., Stieglitz, K.A., Bubunenko, M., Court, D.L., Stec, B., Roberts, M.F.(2007) J Biol Chem 282: 26989-26996
- PubMed: 17652087
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M701210200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2QFL - PubMed Abstract:
The Escherichia coli product of the suhB gene, SuhB, is an inositol monophosphatase (IMPase) that is best known as a suppressor of temperature-sensitive growth phenotypes in E. coli. To gain insights into these biological diverse effects, we determined the structure of the SuhB R184A mutant protein. The structure showed a dimer organization similar to other IMPases, but with an altered interface suggesting that the presence of Arg-184 in the wild-type protein could shift the monomer-dimer equilibrium toward monomer. In parallel, a gel shift assay showed that SuhB forms a tight complex with RNA polymerase (RNA pol) that inhibits the IMPase catalytic activity of SuhB. A variety of SuhB mutant proteins designed to stabilize the dimer interface did not show a clear correlation with the ability of a specific mutant protein to complement the DeltasuhB mutation when introduced extragenically despite being active IMPases. However, the loss of sensitivity to RNA pol binding, i.e. in G173V, R184I, and L96F/R184I, did correlate strongly with loss of complementation of DeltasuhB. Because residue 184 forms the core of the SuhB dimer, it is likely that the interaction with RNA polymerase requires monomeric SuhB. The exposure of specific residues facilitates the interaction of SuhB with RNA pol (or another target with a similar binding surface) and it is this heterodimer formation that is critical to the ability of SuhB to rescue temperature-sensitive phenotypes in E. coli.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Merkert Chemistry Center, Boston College, Chestnut Hill, Massachusetts 02467.