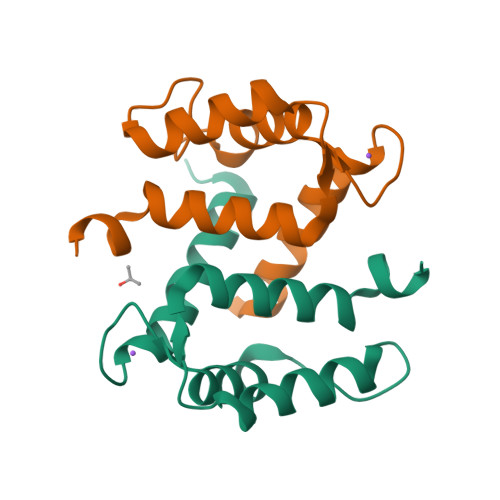
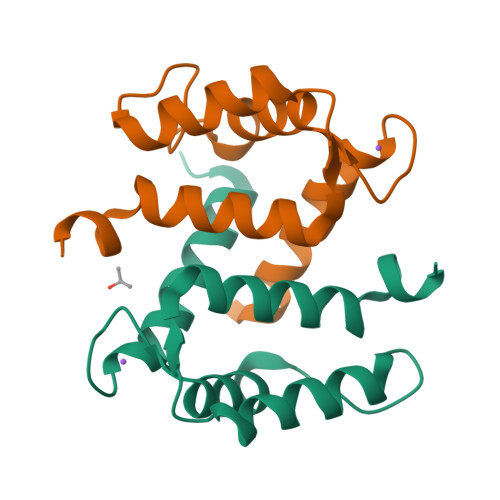
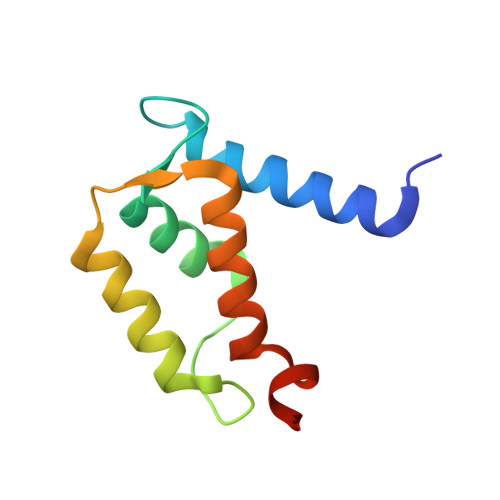
Crystal structure of Ca2+ -free S100A2 at 1.6-A resolution.
Koch, M., Diez, J., Fritz, G.(2008) J Mol Biology 378: 931-940
- PubMed: 18394645
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2008.03.019
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2RGI - PubMed Abstract:
S100A2 is an EF hand-containing Ca(2+)-binding protein of the family of S100 proteins. The protein is localized exclusively in the nucleus and is involved in cell cycle regulation. It attracted most interest by its function as a tumor suppressor via p53 interaction. We determined the crystal structure of homodimeric S100A2 in the Ca(2+)-free state at 1.6-A resolution. The structure revealed structural differences between subunits A and B, especially in the conformation of a loop that connects the N- and C-terminal EF hands and represents a part of the target-binding site in S100 proteins. Analysis of the hydrogen bonding network and molecular dynamics calculations indicate that one of the two observed conformations is more stable. The structure revealed Na(+) bound to each N-terminal EF hand of both subunits coordinated by oxygen atoms of the backbone carbonyl and water molecules. Comparison with the structures of Ca(2+)-free S100A3 and S100A6 suggests that Na(+) might occupy the S100-specific EF hand in the Ca(2+)-free state.
Organizational Affiliation:
Fachbereich Biologie, Universität Konstanz, Postfach M665, Universitätsstrasse 10, 78457 Konstanz, Germany.