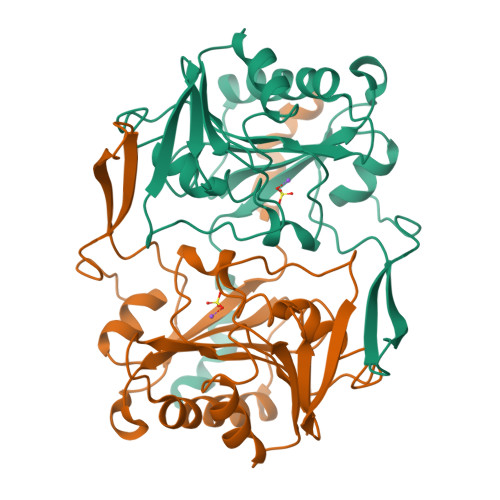
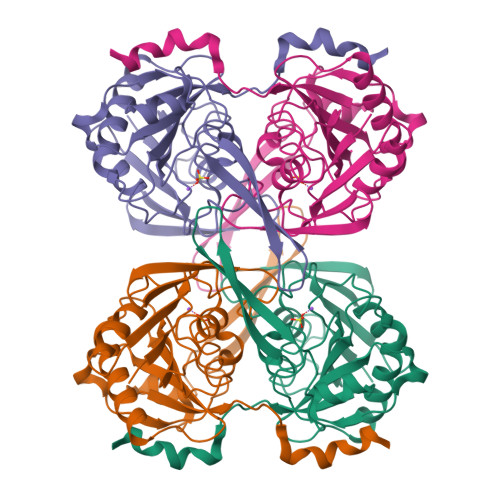
Structure of Sure Protein from Aquifex Aeolicus Vf5 at 1.5 A Resolution.
Antonyuk, S.V., Ellis, M.J., Strange, R.W., Bessho, Y., Kuramitsu, S., Shinkai, A., Yokoyama, S., Hasnain, S.S.(2009) Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 65: 1204
- PubMed: 20054112
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1744309109043814
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2WQK - PubMed Abstract:
SurE is a stationary-phase survival protein found in bacteria, eukaryotes and archaea that exhibits a divalent-metal-ion-dependent phosphatase activity and acts as a nucleotidase and polyphosphate phosphohydrolase. The structure of the SurE protein from the hyperthermophile Aquifex aeolicus has been solved at 1.5 A resolution using molecular replacement with one dimer in the asymmetric unit and refined to an R factor of 15.6%. The crystal packing reveals that two dimers assemble to form a tetramer, although gel-filtration chromatography showed the presence of only a dimer in solution. The phosphatase active-site pocket was occupied by sulfate ions from the crystallization medium.
Organizational Affiliation:
Molecular Biophysics Group, School of Biological Sciences, University of Liverpool, Crown Street, Liverpool L69 7ZB, England.