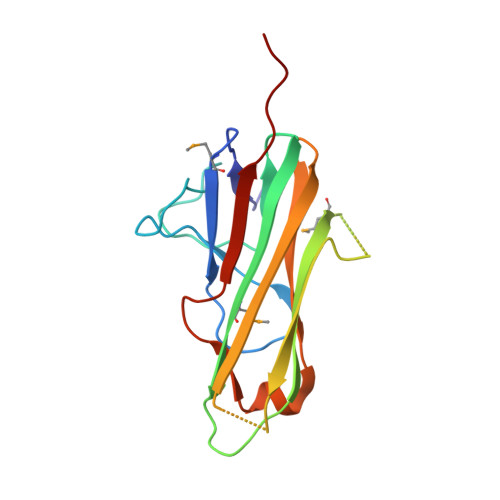
The Structure of the Trimer of Human 4-1Bb Ligand is Unique Among Members of the Tumor Necrosis Factor Superfamily.
Won, E.Y., Cha, K., Byun, J.S., Kim, D.U., Shin, S., Ahn, B., Kim, Y.H., Rice, A.J., Walz, T., Kwon, B.S., Cho, H.S.(2010) J Biol Chem 285: 9202
- PubMed: 20032458
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.084442
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
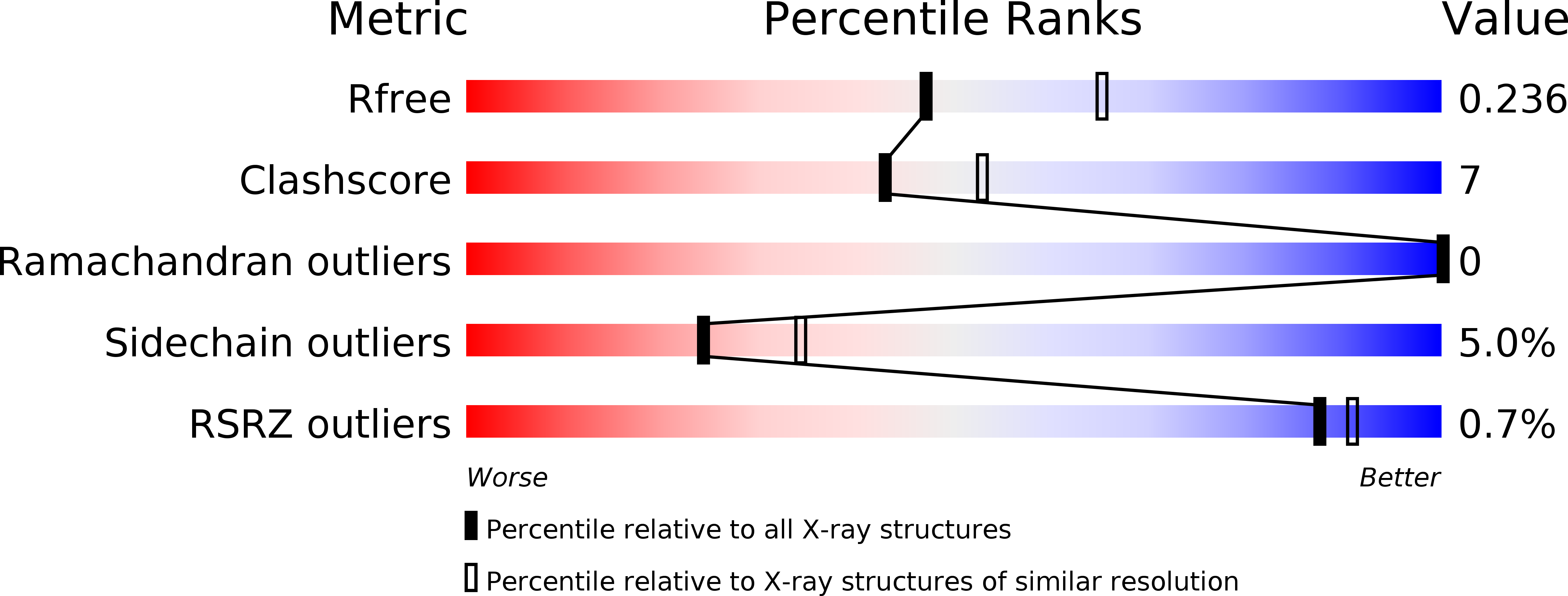
2X29 - PubMed Abstract:
Binding of the 4-1BB ligand (4-1BBL) to its receptor, 4-1BB, provides the T lymphocyte with co-stimulatory signals for survival, proliferation, and differentiation. Importantly, the 4-1BB-4-1BBL pathway is a well known target for anti-cancer immunotherapy. Here we present the 2.3-A crystal structure of the extracellular domain of human 4-1BBL. The ectodomain forms a homotrimer with an extended, three-bladed propeller structure that differs from trimers formed by other members of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily. Based on the 4-1BBL structure, we modeled its complex with 4-1BB, which was consistent with images obtained by electron microscopy, and verified the binding site by site-directed mutagenesis. This structural information will facilitate the development of immunotherapeutics targeting 4-1BB.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biology, Yonsei University, 134 Shinchon-dong, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul 120-749, Korea.