3-Keto-5-Aminohexanoate Cleavage Enzyme: A Common Fold for an Uncommon Claisen-Type Condensation.
Bellinzoni, M., Bastard, K., Perret, A., Zaparucha, A., Perchat, N., Vergne, C., Wagner, T., De Melo-Minardi, R.C., Artiguenave, F., Cohen, G.N., Weissenbach, J., Salanoubat, M., Alzari, P.M.(2011) J Biol Chem 286: 27399
- PubMed: 21632536
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.253260
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
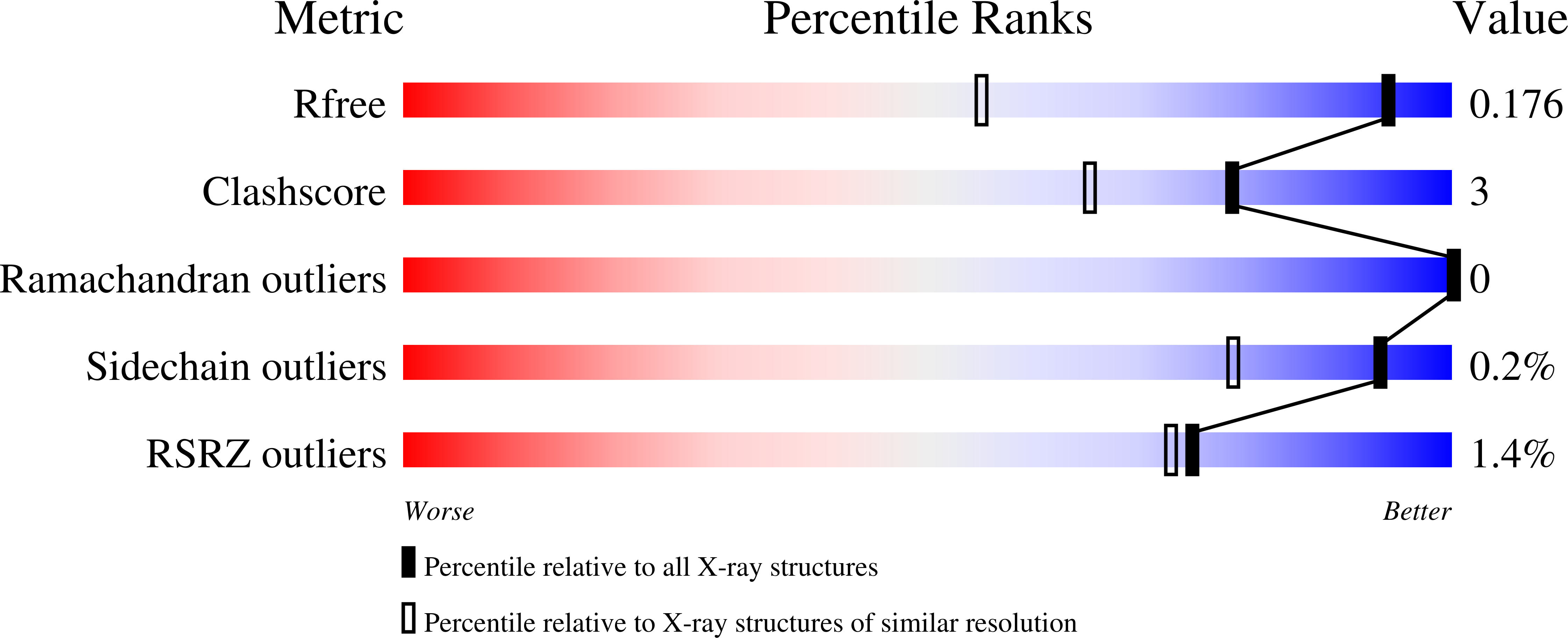
2Y7D, 2Y7E, 2Y7F, 2Y7G - PubMed Abstract:
The exponential increase in genome sequencing output has led to the accumulation of thousands of predicted genes lacking a proper functional annotation. Among this mass of hypothetical proteins, enzymes catalyzing new reactions or using novel ways to catalyze already known reactions might still wait to be identified. Here, we provide a structural and biochemical characterization of the 3-keto-5-aminohexanoate cleavage enzyme (Kce), an enzymatic activity long known as being involved in the anaerobic fermentation of lysine but whose catalytic mechanism has remained elusive so far. Although the enzyme shows the ubiquitous triose phosphate isomerase (TIM) barrel fold and a Zn(2+) cation reminiscent of metal-dependent class II aldolases, our results based on a combination of x-ray snapshots and molecular modeling point to an unprecedented mechanism that proceeds through deprotonation of the 3-keto-5-aminohexanoate substrate, nucleophilic addition onto an incoming acetyl-CoA, intramolecular transfer of the CoA moiety, and final retro-Claisen reaction leading to acetoacetate and 3-aminobutyryl-CoA. This model also accounts for earlier observations showing the origin of carbon atoms in the products, as well as the absence of detection of any covalent acyl-enzyme intermediate. Kce is the first representative of a large family of prokaryotic hypothetical proteins, currently annotated as the "domain of unknown function" DUF849.
Organizational Affiliation:
Unité de Microbiologie Structurale, Institut Pasteur, and CNRS-URA2185, 25 rue du Dr. Roux, 75724 Paris Cedex 15, France.